How Do Money Markets Like Aave and Compound Function?
Money markets such as Aave and Compound are foundational elements of the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, transforming traditional lending and borrowing into a blockchain-based, peer-to-peer process. These platforms leverage smart contracts—self-executing contracts with coded rules—to facilitate secure, transparent transactions without intermediaries like banks. Understanding how these platforms operate provides insight into their role in democratizing access to financial services.
The Core Mechanism of DeFi Money Markets
At their core, Aave and Compound enable users to lend cryptocurrencies to earn interest or borrow assets by providing collateral. Unlike traditional banking systems that rely on centralized institutions, DeFi money markets operate on blockchain networks—primarily Ethereum—using smart contracts that automatically manage lending pools, interest rates, collateralization ratios, and liquidation processes.
When a user deposits assets into these platforms (for example, stablecoins or ETH), they become part of a liquidity pool accessible by borrowers. Borrowers can then take out loans against their collateralized assets at prevailing interest rates determined dynamically by supply and demand within the platform. This system ensures continuous liquidity flow while maintaining transparency through open-source code visible on the blockchain.
Lending and Borrowing Processes
The lending process involves depositing specific cryptocurrencies into the platform’s liquidity pools. Lenders receive interest payments based on the utilization rate of those pools—a metric influenced by borrower activity. For instance:
- Aave: Offers a wide range of assets for lending including stablecoins like USDC or DAI as well as more volatile tokens like ETH.
- Compound: Focuses heavily on stablecoins but also supports other tokens for both lending and borrowing.
Borrowers initiate loans by locking up collateral exceeding the value of borrowed funds (over-collateralization). This safeguard minimizes risk for lenders but requires borrowers to maintain sufficient collateral levels; if asset prices fall below certain thresholds, liquidation occurs automatically via smart contracts.
Interest Rates & Dynamic Pricing
Interest rates in DeFi money markets are not fixed; instead they fluctuate based on market conditions:
- When demand for borrowing increases relative to supply, interest rates rise.
- Conversely, when there is excess liquidity with fewer borrowers, rates decrease.
This dynamic pricing mechanism helps balance supply and demand efficiently without manual intervention from platform operators—a key advantage over traditional financial systems where fixed-rate products dominate.
Governance & Community Involvement
Both Aave and Compound adopt decentralized governance models where token holders influence platform development through voting rights:
- Aave’s governance is primarily driven by its native LEND token (which has transitioned to AAVE tokens), allowing holders to propose upgrades or changes.
- Compound relies on its COMP token for similar purposes.
This community-driven approach promotes transparency but also introduces risks related to governance attacks if large stakeholders act maliciously or disproportionately influence decisions.
Security Challenges & Regulatory Considerations
Despite their innovative nature, DeFi money markets face significant security challenges. Notably:
- In 2020, Aave experienced a security breach resulting in thefts worth approximately $1.4 million due to vulnerabilities exploited within its smart contract infrastructure.
Such incidents underscore the importance of rigorous code audits and ongoing security assessments in safeguarding user funds. Additionally, regulatory scrutiny has increased globally; jurisdictions like the United States have begun examining DeFi protocols’ compliance with existing laws related to securities or anti-money laundering regulations—which could impact future operations significantly.
Market Volatility Impact
Market volatility remains another critical factor influencing these platforms’ stability:
- Fluctuations in cryptocurrency prices can trigger liquidations if collateral values drop too low.
- During periods of high volatility—such as during COVID-related market downturns—the usage patterns often shift dramatically as users seek safety or exit positions quickly.
These dynamics highlight both opportunities—for earning high yields during bullish phases—and risks associated with sudden downturns affecting borrower solvency or lender confidence.
Innovation Driving Growth Despite Challenges
Despite hurdles—including regulatory uncertainty and security concerns—Aave and Compound continue innovating within DeFi space:
- Aave's GHO Stablecoin: An upcoming decentralized stablecoin aims at providing an additional store-of-value option within DeFi ecosystems.
Their ongoing development efforts aim at improving user experience through better interfaces while expanding asset support for broader participation across different crypto communities worldwide.
Key Takeaways About How Money Markets Function
Understanding how platforms like Aave and Compound work involves recognizing several core principles:
- They operate via smart contracts that automate lending/borrowing processes securely without intermediaries.
- Interest rates are dynamic—they adjust according to real-time market conditions driven by supply-demand mechanics.
- Users participate either as lenders earning passive income or borrowers seeking liquidity against crypto collateral.
- Governance is community-driven through token-based voting mechanisms involving stakeholders' active participation.
- Security remains paramount; continuous audits help mitigate risks stemming from potential vulnerabilities inherent in complex codebases.
Future Outlook for Decentralized Money Markets
The future success of money markets such as Aave and Compound hinges upon addressing current challenges while capitalizing on growth opportunities:
- Regulatory clarity will be crucial; clearer legal frameworks could foster wider adoption but may impose constraints requiring adaptation from protocols
- Enhanced security measures—including advanced auditing practices—are essential for maintaining user trust
- Market volatility management tools might evolve further enabling safer participation during turbulent periods
- Continued innovation around new financial primitives (like decentralized stablecoins) will expand utility
By balancing innovation with risk management strategies rooted in transparency—and fostering active community engagement—these platforms can solidify their roles within global finance infrastructure.
This comprehensive overview offers insights aligned with what users seek when exploring how decentralized money markets function — emphasizing operational mechanisms backed by robust technology while acknowledging ongoing challenges faced along this transformative journey toward mainstream adoption in digital finance environments


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-14 12:12
How do money markets like Aave or Compound function?
How Do Money Markets Like Aave and Compound Function?
Money markets such as Aave and Compound are foundational elements of the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, transforming traditional lending and borrowing into a blockchain-based, peer-to-peer process. These platforms leverage smart contracts—self-executing contracts with coded rules—to facilitate secure, transparent transactions without intermediaries like banks. Understanding how these platforms operate provides insight into their role in democratizing access to financial services.
The Core Mechanism of DeFi Money Markets
At their core, Aave and Compound enable users to lend cryptocurrencies to earn interest or borrow assets by providing collateral. Unlike traditional banking systems that rely on centralized institutions, DeFi money markets operate on blockchain networks—primarily Ethereum—using smart contracts that automatically manage lending pools, interest rates, collateralization ratios, and liquidation processes.
When a user deposits assets into these platforms (for example, stablecoins or ETH), they become part of a liquidity pool accessible by borrowers. Borrowers can then take out loans against their collateralized assets at prevailing interest rates determined dynamically by supply and demand within the platform. This system ensures continuous liquidity flow while maintaining transparency through open-source code visible on the blockchain.
Lending and Borrowing Processes
The lending process involves depositing specific cryptocurrencies into the platform’s liquidity pools. Lenders receive interest payments based on the utilization rate of those pools—a metric influenced by borrower activity. For instance:
- Aave: Offers a wide range of assets for lending including stablecoins like USDC or DAI as well as more volatile tokens like ETH.
- Compound: Focuses heavily on stablecoins but also supports other tokens for both lending and borrowing.
Borrowers initiate loans by locking up collateral exceeding the value of borrowed funds (over-collateralization). This safeguard minimizes risk for lenders but requires borrowers to maintain sufficient collateral levels; if asset prices fall below certain thresholds, liquidation occurs automatically via smart contracts.
Interest Rates & Dynamic Pricing
Interest rates in DeFi money markets are not fixed; instead they fluctuate based on market conditions:
- When demand for borrowing increases relative to supply, interest rates rise.
- Conversely, when there is excess liquidity with fewer borrowers, rates decrease.
This dynamic pricing mechanism helps balance supply and demand efficiently without manual intervention from platform operators—a key advantage over traditional financial systems where fixed-rate products dominate.
Governance & Community Involvement
Both Aave and Compound adopt decentralized governance models where token holders influence platform development through voting rights:
- Aave’s governance is primarily driven by its native LEND token (which has transitioned to AAVE tokens), allowing holders to propose upgrades or changes.
- Compound relies on its COMP token for similar purposes.
This community-driven approach promotes transparency but also introduces risks related to governance attacks if large stakeholders act maliciously or disproportionately influence decisions.
Security Challenges & Regulatory Considerations
Despite their innovative nature, DeFi money markets face significant security challenges. Notably:
- In 2020, Aave experienced a security breach resulting in thefts worth approximately $1.4 million due to vulnerabilities exploited within its smart contract infrastructure.
Such incidents underscore the importance of rigorous code audits and ongoing security assessments in safeguarding user funds. Additionally, regulatory scrutiny has increased globally; jurisdictions like the United States have begun examining DeFi protocols’ compliance with existing laws related to securities or anti-money laundering regulations—which could impact future operations significantly.
Market Volatility Impact
Market volatility remains another critical factor influencing these platforms’ stability:
- Fluctuations in cryptocurrency prices can trigger liquidations if collateral values drop too low.
- During periods of high volatility—such as during COVID-related market downturns—the usage patterns often shift dramatically as users seek safety or exit positions quickly.
These dynamics highlight both opportunities—for earning high yields during bullish phases—and risks associated with sudden downturns affecting borrower solvency or lender confidence.
Innovation Driving Growth Despite Challenges
Despite hurdles—including regulatory uncertainty and security concerns—Aave and Compound continue innovating within DeFi space:
- Aave's GHO Stablecoin: An upcoming decentralized stablecoin aims at providing an additional store-of-value option within DeFi ecosystems.
Their ongoing development efforts aim at improving user experience through better interfaces while expanding asset support for broader participation across different crypto communities worldwide.
Key Takeaways About How Money Markets Function
Understanding how platforms like Aave and Compound work involves recognizing several core principles:
- They operate via smart contracts that automate lending/borrowing processes securely without intermediaries.
- Interest rates are dynamic—they adjust according to real-time market conditions driven by supply-demand mechanics.
- Users participate either as lenders earning passive income or borrowers seeking liquidity against crypto collateral.
- Governance is community-driven through token-based voting mechanisms involving stakeholders' active participation.
- Security remains paramount; continuous audits help mitigate risks stemming from potential vulnerabilities inherent in complex codebases.
Future Outlook for Decentralized Money Markets
The future success of money markets such as Aave and Compound hinges upon addressing current challenges while capitalizing on growth opportunities:
- Regulatory clarity will be crucial; clearer legal frameworks could foster wider adoption but may impose constraints requiring adaptation from protocols
- Enhanced security measures—including advanced auditing practices—are essential for maintaining user trust
- Market volatility management tools might evolve further enabling safer participation during turbulent periods
- Continued innovation around new financial primitives (like decentralized stablecoins) will expand utility
By balancing innovation with risk management strategies rooted in transparency—and fostering active community engagement—these platforms can solidify their roles within global finance infrastructure.
This comprehensive overview offers insights aligned with what users seek when exploring how decentralized money markets function — emphasizing operational mechanisms backed by robust technology while acknowledging ongoing challenges faced along this transformative journey toward mainstream adoption in digital finance environments
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Time Oracles Differ from Price Oracles?
Understanding the core components of blockchain technology is essential for anyone involved in decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contracts, or blockchain development. Among these components, oracles play a pivotal role by providing external data to smart contracts, enabling them to interact with real-world information. While all oracles serve as bridges between off-chain data and on-chain execution, they can be broadly categorized into two types: time oracles and price oracles. This article explores their differences, functions, recent advancements, and potential risks to give you a comprehensive understanding of how each contributes to the integrity and efficiency of blockchain ecosystems.
What Are Blockchain Oracles?
Blockchain oracles are specialized systems that feed external data into smart contracts running on blockchain networks. Since blockchains are inherently isolated from the outside world for security reasons—often referred to as being "trustless"—they require trusted sources of information to execute complex operations like financial transactions, insurance claims, or voting mechanisms. These sources can include weather reports, sports scores, stock prices, timestamps, and more.
Oracles act as intermediaries that fetch this data from various off-chain sources and deliver it securely onto the chain where smart contracts can process it automatically based on predefined rules. Their reliability directly impacts the performance and trustworthiness of decentralized applications (dApps).
What Are Time Oracles?
Time oracles specialize in providing accurate timestamps within a blockchain environment. They supply precise date and time information necessary for executing time-sensitive operations in smart contracts. For example:
- DeFi protocols may use time oracles to trigger interest payments at specific intervals.
- NFT marketplaces might rely on timestamps for auction deadlines.
- Gaming platforms could utilize them for event scheduling.
The importance of accurate timing cannot be overstated; even minor discrepancies can lead to unfair advantages or operational failures.
Why Are Time Oracles Important?
In decentralized applications where fairness depends heavily on timing—such as auctions or lending agreements—time accuracy ensures transparency and prevents manipulation. For instance:
- If a timestamp is manipulated early in an auction process due to unreliable oracle data, it could allow malicious actors to gain unfair bidding advantages.
- In financial protocols like loans with fixed repayment schedules triggered by specific dates — inaccurate timestamps could cause delays leading either to missed payments or premature executions.
Recent Developments in Time Oracle Technology
Advances have been made toward creating more secure and reliable solutions:
Blockchain-integrated solutions: Some platforms now embed native time oracle functionalities directly within their protocols.
Decentralized approaches: Decentralized time oracle networks distribute trust among multiple nodes rather than relying on centralized authorities; this enhances security against tampering attempts.
Regulatory compliance focus: As legal frameworks evolve around digital assets requiring precise timestamping—for example in securities trading—the development of compliant solutions has gained momentum.
What Are Price Oracles?
Price oracles provide real-time market data such as cryptocurrency prices (e.g., Bitcoin/USD), stock indices (e.g., S&P 500), commodity prices (e.g., gold), among others. They are fundamental for DeFi applications that depend heavily on current market conditions:
Lending platforms adjust collateral requirements based on asset prices.
Stablecoins maintain peg values through price feeds.
Derivatives trading relies entirely upon accurate pricing inputs fed via price oracles.
The Significance of Accurate Price Data
Inaccurate pricing feeds pose significant risks:
Market Manipulation: Malicious actors may attempt "oracle attacks" by feeding false data into the system—a risk mitigated through aggregation techniques involving multiple independent sources.
Financial Losses: Incorrect prices can cause liquidations at unfavorable rates leading either to unnecessary losses for users—or worse—in extreme cases causing systemic failures within DeFi ecosystems.
Operational Inefficiencies: Delayed updates due to slow data retrieval impact protocol responsiveness during volatile markets when timely decisions are crucial.
Innovations Enhancing Price Oracle Reliability
Recent trends aim at improving accuracy while reducing vulnerabilities:
Data Aggregation Services: Combining multiple independent sources reduces reliance on any single point that might be compromised—a technique known as decentralized aggregation.
Machine Learning Integration: Some projects incorporate machine learning algorithms capable of predicting short-term market movements which help smooth out anomalies caused by sudden spikes/drops.
Enhanced Security Protocols: Cryptographic techniques such as threshold signatures ensure only validated data reaches smart contracts; decentralization further minimizes hacking risks.
Comparing Time vs Price Oracles: Key Differences
While both types serve critical roles within blockchain ecosystems—they differ significantly across several dimensions including purpose, implementation complexity—and associated risks:
| Aspect | Time Oracles | Price Oricles |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provide accurate timestamps | Deliver real-time market prices |
| Data Nature | Static but critical temporal info | Dynamic financial metrics |
| Impact Area | Timing-dependent operations like scheduling & fairness | Financial transactions & asset valuation |
| Accuracy Requirements | Extremely high precision needed; milliseconds matter | High accuracy vital but tolerates slight delays during volatile periods |
| Security Concerns | Manipulation leads mainly to incorrect execution timing | Market manipulation poses significant financial risk |
Understanding these distinctions helps developers choose appropriate oracle solutions aligned with their application's needs while implementing necessary safeguards against potential vulnerabilities.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Both Oracle Types
Despite technological advances—such as decentralization efforts—the deployment remains susceptible under certain conditions:
Common Risks
- Data Manipulation: Attackers may compromise source feeds leading either directly—or indirectly—to incorrect contract execution outcomes;
- Centralization Vulnerabilities: Reliance upon single entities increases attack surface;
- Latency Issues: Delays in fetching updated info especially during high volatility periods;
- Regulatory Compliance: Legal frameworks demanding verifiable timestamping impose additional constraints;
Specific Concerns
For time oases, incorrect timestamps could result in early/late contract triggers affecting user funds' safety; whereas price oases face threats from flash loan attacks designed specifically targeting vulnerable price feeds causing cascading failures across DeFi protocols.
How Blockchain Ecosystems Address These Challenges
To mitigate these issues:
- Developers increasingly adopt decentralized architectures involving multiple nodes sharing consensus over provided data,
- Use cryptographic proofs such as zk-SNARKs enhance trustworthiness,
- Regular audits ensure compliance with evolving standards,
- Cross-source verification improves resilience against manipulation,
These measures collectively strengthen overall ecosystem robustness ensuring user confidence remains high despite emerging threats.
Future Outlook for Blockchain Data Feeds
As DeFi continues its rapid growth trajectory—with total value locked surpassing hundreds of billions—the demand for reliable oracle services will intensify accordingly.. Innovations like AI-driven prediction models combined with multi-source aggregation promise smarter security layers while regulatory landscapes push toward standardized practices ensuring transparency and accountability across all oracle implementations.
Final Thoughts
Distinguishing between time versus price oracl es reveals their unique roles yet interconnected importance within decentralized systems.. Ensuring their security involves ongoing technological innovation coupled with rigorous governance standards.. As stakeholders—from developers through regulators—collaborate towards resilient infrastructure design , understanding these differences becomes essential not only for building robust dApps but also safeguarding user assets amidst an ever-changing landscape.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-14 11:34
How do time oracles differ from price oracles?
How Do Time Oracles Differ from Price Oracles?
Understanding the core components of blockchain technology is essential for anyone involved in decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contracts, or blockchain development. Among these components, oracles play a pivotal role by providing external data to smart contracts, enabling them to interact with real-world information. While all oracles serve as bridges between off-chain data and on-chain execution, they can be broadly categorized into two types: time oracles and price oracles. This article explores their differences, functions, recent advancements, and potential risks to give you a comprehensive understanding of how each contributes to the integrity and efficiency of blockchain ecosystems.
What Are Blockchain Oracles?
Blockchain oracles are specialized systems that feed external data into smart contracts running on blockchain networks. Since blockchains are inherently isolated from the outside world for security reasons—often referred to as being "trustless"—they require trusted sources of information to execute complex operations like financial transactions, insurance claims, or voting mechanisms. These sources can include weather reports, sports scores, stock prices, timestamps, and more.
Oracles act as intermediaries that fetch this data from various off-chain sources and deliver it securely onto the chain where smart contracts can process it automatically based on predefined rules. Their reliability directly impacts the performance and trustworthiness of decentralized applications (dApps).
What Are Time Oracles?
Time oracles specialize in providing accurate timestamps within a blockchain environment. They supply precise date and time information necessary for executing time-sensitive operations in smart contracts. For example:
- DeFi protocols may use time oracles to trigger interest payments at specific intervals.
- NFT marketplaces might rely on timestamps for auction deadlines.
- Gaming platforms could utilize them for event scheduling.
The importance of accurate timing cannot be overstated; even minor discrepancies can lead to unfair advantages or operational failures.
Why Are Time Oracles Important?
In decentralized applications where fairness depends heavily on timing—such as auctions or lending agreements—time accuracy ensures transparency and prevents manipulation. For instance:
- If a timestamp is manipulated early in an auction process due to unreliable oracle data, it could allow malicious actors to gain unfair bidding advantages.
- In financial protocols like loans with fixed repayment schedules triggered by specific dates — inaccurate timestamps could cause delays leading either to missed payments or premature executions.
Recent Developments in Time Oracle Technology
Advances have been made toward creating more secure and reliable solutions:
Blockchain-integrated solutions: Some platforms now embed native time oracle functionalities directly within their protocols.
Decentralized approaches: Decentralized time oracle networks distribute trust among multiple nodes rather than relying on centralized authorities; this enhances security against tampering attempts.
Regulatory compliance focus: As legal frameworks evolve around digital assets requiring precise timestamping—for example in securities trading—the development of compliant solutions has gained momentum.
What Are Price Oracles?
Price oracles provide real-time market data such as cryptocurrency prices (e.g., Bitcoin/USD), stock indices (e.g., S&P 500), commodity prices (e.g., gold), among others. They are fundamental for DeFi applications that depend heavily on current market conditions:
Lending platforms adjust collateral requirements based on asset prices.
Stablecoins maintain peg values through price feeds.
Derivatives trading relies entirely upon accurate pricing inputs fed via price oracles.
The Significance of Accurate Price Data
Inaccurate pricing feeds pose significant risks:
Market Manipulation: Malicious actors may attempt "oracle attacks" by feeding false data into the system—a risk mitigated through aggregation techniques involving multiple independent sources.
Financial Losses: Incorrect prices can cause liquidations at unfavorable rates leading either to unnecessary losses for users—or worse—in extreme cases causing systemic failures within DeFi ecosystems.
Operational Inefficiencies: Delayed updates due to slow data retrieval impact protocol responsiveness during volatile markets when timely decisions are crucial.
Innovations Enhancing Price Oracle Reliability
Recent trends aim at improving accuracy while reducing vulnerabilities:
Data Aggregation Services: Combining multiple independent sources reduces reliance on any single point that might be compromised—a technique known as decentralized aggregation.
Machine Learning Integration: Some projects incorporate machine learning algorithms capable of predicting short-term market movements which help smooth out anomalies caused by sudden spikes/drops.
Enhanced Security Protocols: Cryptographic techniques such as threshold signatures ensure only validated data reaches smart contracts; decentralization further minimizes hacking risks.
Comparing Time vs Price Oracles: Key Differences
While both types serve critical roles within blockchain ecosystems—they differ significantly across several dimensions including purpose, implementation complexity—and associated risks:
| Aspect | Time Oracles | Price Oricles |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provide accurate timestamps | Deliver real-time market prices |
| Data Nature | Static but critical temporal info | Dynamic financial metrics |
| Impact Area | Timing-dependent operations like scheduling & fairness | Financial transactions & asset valuation |
| Accuracy Requirements | Extremely high precision needed; milliseconds matter | High accuracy vital but tolerates slight delays during volatile periods |
| Security Concerns | Manipulation leads mainly to incorrect execution timing | Market manipulation poses significant financial risk |
Understanding these distinctions helps developers choose appropriate oracle solutions aligned with their application's needs while implementing necessary safeguards against potential vulnerabilities.
Challenges & Risks Associated With Both Oracle Types
Despite technological advances—such as decentralization efforts—the deployment remains susceptible under certain conditions:
Common Risks
- Data Manipulation: Attackers may compromise source feeds leading either directly—or indirectly—to incorrect contract execution outcomes;
- Centralization Vulnerabilities: Reliance upon single entities increases attack surface;
- Latency Issues: Delays in fetching updated info especially during high volatility periods;
- Regulatory Compliance: Legal frameworks demanding verifiable timestamping impose additional constraints;
Specific Concerns
For time oases, incorrect timestamps could result in early/late contract triggers affecting user funds' safety; whereas price oases face threats from flash loan attacks designed specifically targeting vulnerable price feeds causing cascading failures across DeFi protocols.
How Blockchain Ecosystems Address These Challenges
To mitigate these issues:
- Developers increasingly adopt decentralized architectures involving multiple nodes sharing consensus over provided data,
- Use cryptographic proofs such as zk-SNARKs enhance trustworthiness,
- Regular audits ensure compliance with evolving standards,
- Cross-source verification improves resilience against manipulation,
These measures collectively strengthen overall ecosystem robustness ensuring user confidence remains high despite emerging threats.
Future Outlook for Blockchain Data Feeds
As DeFi continues its rapid growth trajectory—with total value locked surpassing hundreds of billions—the demand for reliable oracle services will intensify accordingly.. Innovations like AI-driven prediction models combined with multi-source aggregation promise smarter security layers while regulatory landscapes push toward standardized practices ensuring transparency and accountability across all oracle implementations.
Final Thoughts
Distinguishing between time versus price oracl es reveals their unique roles yet interconnected importance within decentralized systems.. Ensuring their security involves ongoing technological innovation coupled with rigorous governance standards.. As stakeholders—from developers through regulators—collaborate towards resilient infrastructure design , understanding these differences becomes essential not only for building robust dApps but also safeguarding user assets amidst an ever-changing landscape.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is HotStuff Consensus?
HotStuff is a cutting-edge consensus algorithm specifically designed for blockchain networks, aiming to improve scalability, security, and efficiency in distributed systems. Developed by researchers from UCLA and UC Berkeley in 2019, it has quickly gained recognition for its innovative approach to solving some of the longstanding challenges faced by traditional blockchain consensus mechanisms.
At its core, HotStuff is a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) protocol that ensures network agreement even when some nodes act maliciously or fail unexpectedly. Its design principles focus on creating a system that can handle high transaction throughput while maintaining robust security guarantees. This makes it particularly suitable for large-scale applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi), enterprise blockchains, and other distributed ledger technologies.
How Does HotStuff Work?
HotStuff operates through a series of rounds where nodes collaborate to agree on the next block to add to the blockchain. The process begins with a designated leader node proposing a block during each round. Other nodes then vote on this proposal based on predefined rules and cryptographic signatures that validate their approval.
One of the key features of HotStuff is its pipelined architecture, which allows multiple consensus rounds to be processed concurrently. This significantly reduces latency compared to earlier algorithms like PBFT (Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance). The leader election process is randomized each round—ensuring no single node maintains control over time—thus promoting decentralization and fairness within the network.
The protocol also incorporates timeout mechanisms; if the leader fails or behaves maliciously, other nodes can initiate view changes or elect new leaders without halting progress. These features collectively contribute to HotStuff's high fault tolerance — capable of withstanding up to one-third faulty or malicious nodes without compromising network integrity.
Why Is Scalability Important in Blockchain?
As blockchain networks expand in size and complexity, traditional consensus algorithms often struggle with performance bottlenecks. Protocols like PBFT require multiple communication rounds among all participating nodes—a process that becomes increasingly inefficient as more participants join.
HotStuff addresses these scalability issues through its pipelined approach which minimizes communication overhead by overlapping multiple consensus phases across different blocks simultaneously. This design enables higher throughput—measured in transactions per second—and lower latency times necessary for real-time applications such as DeFi platforms or enterprise solutions handling thousands of transactions daily.
Furthermore, hotstuff’s ability to operate efficiently across geographically dispersed nodes makes it suitable for global networks where speed and reliability are critical factors influencing user experience and operational costs.
Ensuring Security Through Fault Tolerance
Security remains paramount in any blockchain system because it protects against double-spending attacks, censorship attempts, or malicious behavior from compromised nodes. HotStuff enhances security via cryptographic signatures combined with voting mechanisms that require more than two-thirds majority approval before adding new blocks—a standard threshold ensuring resilience against Byzantine actors.
Additionally, its timeout-based strategies enable quick detection of faulty leaders or suspicious activity within the network. When anomalies are detected—such as inconsistent votes—the protocol triggers view changes where new leaders are elected seamlessly without disrupting ongoing operations.
This combination of fault tolerance techniques ensures that even under adverse conditions—including targeted attacks—the integrity and consistency of the blockchain are maintained reliably over time.
Recent Developments & Adoption
Since its initial publication in 2019 by UCLA and UC Berkeley researchers (Yin et al., 2019), HotStuff has seen significant interest from both academia and industry sectors seeking scalable solutions for distributed ledgers. Developers have implemented prototypes based on HotStuff’s specifications; these implementations have demonstrated promising results regarding performance metrics like transaction speed and robustness under stress tests [2].
Several prominent projects have integrated HotStuff into their architectures due to these advantages:
- Decentralized Finance Platforms: Some DeFi protocols leverage HotStuff’s efficiency for handling high-volume trading activities.
- Enterprise Blockchains: Businesses adopting private permissioned ledgers benefit from hotstuff's fault-tolerant properties.
- Research & Development: Ongoing studies aim at refining leader election processes further while addressing potential centralization risks [4].
However, challenges remain—particularly around ensuring truly decentralized leadership through secure election mechanisms [4]. If not carefully managed, there exists potential risk toward centralization if certain entities dominate leadership roles due to resource advantages or vulnerabilities within election protocols.
Challenges Facing HotStuf Implementation
While promising overall results position HotStuff as an industry-standard BFT algorithm candidate moving forward; several hurdles need addressing:
Leader Election Robustness: Ensuring fair randomness so no single entity consistently controls leadership remains complex but crucial.
Potential Centralization Risks: Without proper safeguards during leader selection processes—which could favor well-resourced participants—the system might drift toward centralization.
Network Partitioning & Failures: Handling extreme cases such as network splits requires sophisticated fallback strategies beyond current designs.
Addressing these issues involves ongoing research into more resilient election algorithms coupled with rigorous testing across diverse environments—all vital steps toward mainstream adoption [4].
The Future Outlook for Hotstuff
Given its proven capabilities in enhancing scalability while maintaining strong security guarantees—and backed by active development communities—Hotstuff stands poised as an influential player among next-generation consensus protocols [1][3]. Its adoption across various sectors indicates growing confidence among developers seeking efficient alternatives beyond legacy algorithms like PBFT or Proof-of-Work systems prone to energy inefficiency.
Continued research efforts aim at optimizing leader election methods further while safeguarding decentralization principles—a balancing act essential for widespread acceptance within permissionless public blockchains versus controlled enterprise settings alike [4].
In summary,
Hotstuff represents an important evolution towards scalable yet secure distributed ledger technology capable of supporting complex applications at scale—with ongoing innovations likely shaping future standards in blockchain consensus mechanisms.
References
- Yin et al., "Hot Stuff: BFT in 2 Seconds," ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing (2019).
- Implementation details available at GitHub repository https://github.com/ucb-bar/hotstuff.
- Industry adoption insights reported by CoinDesk (2023).
- Research discussing challenges related to leader election published on ResearchGate (2022).


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-14 11:05
What is HotStuff consensus?
What Is HotStuff Consensus?
HotStuff is a cutting-edge consensus algorithm specifically designed for blockchain networks, aiming to improve scalability, security, and efficiency in distributed systems. Developed by researchers from UCLA and UC Berkeley in 2019, it has quickly gained recognition for its innovative approach to solving some of the longstanding challenges faced by traditional blockchain consensus mechanisms.
At its core, HotStuff is a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) protocol that ensures network agreement even when some nodes act maliciously or fail unexpectedly. Its design principles focus on creating a system that can handle high transaction throughput while maintaining robust security guarantees. This makes it particularly suitable for large-scale applications such as decentralized finance (DeFi), enterprise blockchains, and other distributed ledger technologies.
How Does HotStuff Work?
HotStuff operates through a series of rounds where nodes collaborate to agree on the next block to add to the blockchain. The process begins with a designated leader node proposing a block during each round. Other nodes then vote on this proposal based on predefined rules and cryptographic signatures that validate their approval.
One of the key features of HotStuff is its pipelined architecture, which allows multiple consensus rounds to be processed concurrently. This significantly reduces latency compared to earlier algorithms like PBFT (Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance). The leader election process is randomized each round—ensuring no single node maintains control over time—thus promoting decentralization and fairness within the network.
The protocol also incorporates timeout mechanisms; if the leader fails or behaves maliciously, other nodes can initiate view changes or elect new leaders without halting progress. These features collectively contribute to HotStuff's high fault tolerance — capable of withstanding up to one-third faulty or malicious nodes without compromising network integrity.
Why Is Scalability Important in Blockchain?
As blockchain networks expand in size and complexity, traditional consensus algorithms often struggle with performance bottlenecks. Protocols like PBFT require multiple communication rounds among all participating nodes—a process that becomes increasingly inefficient as more participants join.
HotStuff addresses these scalability issues through its pipelined approach which minimizes communication overhead by overlapping multiple consensus phases across different blocks simultaneously. This design enables higher throughput—measured in transactions per second—and lower latency times necessary for real-time applications such as DeFi platforms or enterprise solutions handling thousands of transactions daily.
Furthermore, hotstuff’s ability to operate efficiently across geographically dispersed nodes makes it suitable for global networks where speed and reliability are critical factors influencing user experience and operational costs.
Ensuring Security Through Fault Tolerance
Security remains paramount in any blockchain system because it protects against double-spending attacks, censorship attempts, or malicious behavior from compromised nodes. HotStuff enhances security via cryptographic signatures combined with voting mechanisms that require more than two-thirds majority approval before adding new blocks—a standard threshold ensuring resilience against Byzantine actors.
Additionally, its timeout-based strategies enable quick detection of faulty leaders or suspicious activity within the network. When anomalies are detected—such as inconsistent votes—the protocol triggers view changes where new leaders are elected seamlessly without disrupting ongoing operations.
This combination of fault tolerance techniques ensures that even under adverse conditions—including targeted attacks—the integrity and consistency of the blockchain are maintained reliably over time.
Recent Developments & Adoption
Since its initial publication in 2019 by UCLA and UC Berkeley researchers (Yin et al., 2019), HotStuff has seen significant interest from both academia and industry sectors seeking scalable solutions for distributed ledgers. Developers have implemented prototypes based on HotStuff’s specifications; these implementations have demonstrated promising results regarding performance metrics like transaction speed and robustness under stress tests [2].
Several prominent projects have integrated HotStuff into their architectures due to these advantages:
- Decentralized Finance Platforms: Some DeFi protocols leverage HotStuff’s efficiency for handling high-volume trading activities.
- Enterprise Blockchains: Businesses adopting private permissioned ledgers benefit from hotstuff's fault-tolerant properties.
- Research & Development: Ongoing studies aim at refining leader election processes further while addressing potential centralization risks [4].
However, challenges remain—particularly around ensuring truly decentralized leadership through secure election mechanisms [4]. If not carefully managed, there exists potential risk toward centralization if certain entities dominate leadership roles due to resource advantages or vulnerabilities within election protocols.
Challenges Facing HotStuf Implementation
While promising overall results position HotStuff as an industry-standard BFT algorithm candidate moving forward; several hurdles need addressing:
Leader Election Robustness: Ensuring fair randomness so no single entity consistently controls leadership remains complex but crucial.
Potential Centralization Risks: Without proper safeguards during leader selection processes—which could favor well-resourced participants—the system might drift toward centralization.
Network Partitioning & Failures: Handling extreme cases such as network splits requires sophisticated fallback strategies beyond current designs.
Addressing these issues involves ongoing research into more resilient election algorithms coupled with rigorous testing across diverse environments—all vital steps toward mainstream adoption [4].
The Future Outlook for Hotstuff
Given its proven capabilities in enhancing scalability while maintaining strong security guarantees—and backed by active development communities—Hotstuff stands poised as an influential player among next-generation consensus protocols [1][3]. Its adoption across various sectors indicates growing confidence among developers seeking efficient alternatives beyond legacy algorithms like PBFT or Proof-of-Work systems prone to energy inefficiency.
Continued research efforts aim at optimizing leader election methods further while safeguarding decentralization principles—a balancing act essential for widespread acceptance within permissionless public blockchains versus controlled enterprise settings alike [4].
In summary,
Hotstuff represents an important evolution towards scalable yet secure distributed ledger technology capable of supporting complex applications at scale—with ongoing innovations likely shaping future standards in blockchain consensus mechanisms.
References
- Yin et al., "Hot Stuff: BFT in 2 Seconds," ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing (2019).
- Implementation details available at GitHub repository https://github.com/ucb-bar/hotstuff.
- Industry adoption insights reported by CoinDesk (2023).
- Research discussing challenges related to leader election published on ResearchGate (2022).
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
What Is Ethereum (ETH) and How Does It Differ from Bitcoin (BTC)?
Understanding the differences between Ethereum and Bitcoin is essential for anyone interested in the cryptocurrency space. Both are leading digital assets, but they serve distinct purposes, operate on different technological foundations, and have unique features that influence their value and use cases. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Ethereum (ETH) and Bitcoin (BTC), highlighting their core functionalities, key distinctions, recent developments, and potential future impacts.
Overview of Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum was launched in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin with the goal of creating a decentralized platform capable of executing smart contracts—self-executing agreements coded directly into blockchain transactions. Unlike Bitcoin’s primary focus as a digital currency or store of value, Ethereum aims to be a versatile blockchain platform that supports decentralized applications (dApps). Its open-source nature allows developers worldwide to build applications ranging from finance to gaming on its network.
One of Ethereum’s most significant innovations is its ability to facilitate programmable contracts through smart contract technology. These contracts automatically execute when predefined conditions are met without intermediaries. This capability has opened up new possibilities for automation across industries such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more.
Key Features That Define Ethereum
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing code embedded within the blockchain that automates complex transactions.
- Decentralized Applications: Apps built on top of the Ethereum network that run without centralized control.
- Gas Fees: A measure called "gas" determines how much computational effort is needed for executing operations; paid in Ether (ETH).
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): The runtime environment responsible for executing smart contracts securely across nodes.
Overview of Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin was created in 2009 by an anonymous individual or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto. It was designed primarily as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system aimed at enabling secure digital transactions without relying on traditional financial institutions or governments. As the first cryptocurrency ever developed, Bitcoin established many foundational principles still relevant today—decentralization, limited supply, transparency through public ledgers.
Bitcoin operates via mining—a process where powerful computers solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add new coins into circulation until reaching its cap at 21 million BTC. Its scarcity model helps maintain value over time while providing incentives for miners who secure the network.
Core Attributes That Define Bitcoin
- Digital Currency Use Case: Primarily used for transferring value globally.
- Decentralized Ledger: All transactions are recorded publicly on the blockchain.
- Limited Supply Cap: Fixed maximum supply ensures scarcity—21 million BTC.
- Mining Process: Proof-of-work consensus mechanism that validates transactions; energy-intensive but highly secure.
Major Differences Between Ethereum and Bitcoin
While both cryptocurrencies leverage blockchain technology's strengths—transparency, security, decentralization—they differ significantly in purpose and technical architecture:
Primary Purpose
- Bitcoin: Acts mainly as digital gold or an alternative investment asset; focuses on being a store of value.
- Ethereum: Functions as a platform enabling decentralized applications via smart contracts; more flexible than just currency transfer.
Blockchain Architecture
- Bitcoin: Uses a relatively simple ledger optimized solely for transaction verification.
- Ethereum: Employs an advanced architecture capable of executing complex scripts through its Turing-complete programming language.
Smart Contract Support
- Bitcoin: Limited scripting capabilities; does not natively support full-fledged smart contracts.
- Ethereum: Built specifically to support sophisticated smart contract development with extensive programmability options.
Transaction Fees & Gas
- Bitcoin: Transaction fees incentivize miners based purely on transaction size; fee levels fluctuate with network congestion.
- Ethereum: Uses gas units representing computational effort required; fees can vary depending on contract complexity during high demand periods.
Scalability Solutions
- Both networks face scalability challenges:
- Bitcoin has implemented solutions like Lightning Network—a second-layer protocol facilitating faster off-chain payments.
- Ethereum is transitioning toward ETH 2.x upgrades featuring proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms designed to improve throughput significantly while reducing energy consumption.
- Both networks face scalability challenges:
Recent Developments Shaping Their Futures
The evolution of both cryptocurrencies reflects ongoing efforts to address existing limitations:
Ethereum 2.x Upgrade
One notable development is Ethereum's transition toward "Ethereum 2.0," which aims to enhance scalability by shifting from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS). This upgrade promises faster transaction processing times ("sharding") while reducing environmental impact—a critical step given increasing concerns about energy consumption associated with PoW systems like current ETH mining processes.
Adoption Trends & Regulatory Environment
In recent years, institutional interest has surged—with products like Bitcoin ETFs gaining approval—and regulatory frameworks continue evolving globally around these assets' legality and usage rights:
The approval process for ETF products could lead mainstream investors into crypto markets further boosting prices but also introducing volatility risks if regulatory policies tighten unexpectedly.
Governments worldwide are exploring regulations around DeFi platforms built atop networks like Ethereum or considering central bank digital currencies inspired by these technologies.
Potential Risks & Challenges Ahead
Despite promising advancements—and growing adoption—the future remains uncertain due to several factors:
Market Volatility
Both ETH and BTC experience significant price swings driven by market sentiment shifts influenced by macroeconomic trends or regulatory news cycles—all typical within emerging asset classes but challenging for investors seeking stability.Security Concerns
As platforms grow larger with more users deploying complex dApps or holding substantial funds online—security vulnerabilities may emerge through coding errors or malicious attacks requiring continuous vigilance from developers.
3.. Competitive Landscape
Other blockchains such as Binance Smart Chain or Solana aim at offering similar functionalities with higher throughput speeds at lower costs—which could challenge Ether’s dominance if they succeed widely.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what differentiates Ethereum from Bitcoin helps investors evaluate their respective roles within broader financial ecosystems better suited either as stores of value—or innovative platforms powering decentralized services worldwide . While both projects face hurdles related to scalability security regulation—they also present tremendous opportunities driven by technological innovation shaping tomorrow’s financial landscape.
By grasping these core aspects—from fundamental purpose through recent upgrades—you can make informed decisions whether you're investing directly in ETH/BTC—or exploring how these pioneering technologies might influence your industry sector moving forward


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-05-11 10:45
What is Ethereum (ETH) and how does it differ from Bitcoin (BTC)?
What Is Ethereum (ETH) and How Does It Differ from Bitcoin (BTC)?
Understanding the differences between Ethereum and Bitcoin is essential for anyone interested in the cryptocurrency space. Both are leading digital assets, but they serve distinct purposes, operate on different technological foundations, and have unique features that influence their value and use cases. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Ethereum (ETH) and Bitcoin (BTC), highlighting their core functionalities, key distinctions, recent developments, and potential future impacts.
Overview of Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum was launched in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin with the goal of creating a decentralized platform capable of executing smart contracts—self-executing agreements coded directly into blockchain transactions. Unlike Bitcoin’s primary focus as a digital currency or store of value, Ethereum aims to be a versatile blockchain platform that supports decentralized applications (dApps). Its open-source nature allows developers worldwide to build applications ranging from finance to gaming on its network.
One of Ethereum’s most significant innovations is its ability to facilitate programmable contracts through smart contract technology. These contracts automatically execute when predefined conditions are met without intermediaries. This capability has opened up new possibilities for automation across industries such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more.
Key Features That Define Ethereum
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing code embedded within the blockchain that automates complex transactions.
- Decentralized Applications: Apps built on top of the Ethereum network that run without centralized control.
- Gas Fees: A measure called "gas" determines how much computational effort is needed for executing operations; paid in Ether (ETH).
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): The runtime environment responsible for executing smart contracts securely across nodes.
Overview of Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin was created in 2009 by an anonymous individual or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto. It was designed primarily as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system aimed at enabling secure digital transactions without relying on traditional financial institutions or governments. As the first cryptocurrency ever developed, Bitcoin established many foundational principles still relevant today—decentralization, limited supply, transparency through public ledgers.
Bitcoin operates via mining—a process where powerful computers solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add new coins into circulation until reaching its cap at 21 million BTC. Its scarcity model helps maintain value over time while providing incentives for miners who secure the network.
Core Attributes That Define Bitcoin
- Digital Currency Use Case: Primarily used for transferring value globally.
- Decentralized Ledger: All transactions are recorded publicly on the blockchain.
- Limited Supply Cap: Fixed maximum supply ensures scarcity—21 million BTC.
- Mining Process: Proof-of-work consensus mechanism that validates transactions; energy-intensive but highly secure.
Major Differences Between Ethereum and Bitcoin
While both cryptocurrencies leverage blockchain technology's strengths—transparency, security, decentralization—they differ significantly in purpose and technical architecture:
Primary Purpose
- Bitcoin: Acts mainly as digital gold or an alternative investment asset; focuses on being a store of value.
- Ethereum: Functions as a platform enabling decentralized applications via smart contracts; more flexible than just currency transfer.
Blockchain Architecture
- Bitcoin: Uses a relatively simple ledger optimized solely for transaction verification.
- Ethereum: Employs an advanced architecture capable of executing complex scripts through its Turing-complete programming language.
Smart Contract Support
- Bitcoin: Limited scripting capabilities; does not natively support full-fledged smart contracts.
- Ethereum: Built specifically to support sophisticated smart contract development with extensive programmability options.
Transaction Fees & Gas
- Bitcoin: Transaction fees incentivize miners based purely on transaction size; fee levels fluctuate with network congestion.
- Ethereum: Uses gas units representing computational effort required; fees can vary depending on contract complexity during high demand periods.
Scalability Solutions
- Both networks face scalability challenges:
- Bitcoin has implemented solutions like Lightning Network—a second-layer protocol facilitating faster off-chain payments.
- Ethereum is transitioning toward ETH 2.x upgrades featuring proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms designed to improve throughput significantly while reducing energy consumption.
- Both networks face scalability challenges:
Recent Developments Shaping Their Futures
The evolution of both cryptocurrencies reflects ongoing efforts to address existing limitations:
Ethereum 2.x Upgrade
One notable development is Ethereum's transition toward "Ethereum 2.0," which aims to enhance scalability by shifting from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS). This upgrade promises faster transaction processing times ("sharding") while reducing environmental impact—a critical step given increasing concerns about energy consumption associated with PoW systems like current ETH mining processes.
Adoption Trends & Regulatory Environment
In recent years, institutional interest has surged—with products like Bitcoin ETFs gaining approval—and regulatory frameworks continue evolving globally around these assets' legality and usage rights:
The approval process for ETF products could lead mainstream investors into crypto markets further boosting prices but also introducing volatility risks if regulatory policies tighten unexpectedly.
Governments worldwide are exploring regulations around DeFi platforms built atop networks like Ethereum or considering central bank digital currencies inspired by these technologies.
Potential Risks & Challenges Ahead
Despite promising advancements—and growing adoption—the future remains uncertain due to several factors:
Market Volatility
Both ETH and BTC experience significant price swings driven by market sentiment shifts influenced by macroeconomic trends or regulatory news cycles—all typical within emerging asset classes but challenging for investors seeking stability.Security Concerns
As platforms grow larger with more users deploying complex dApps or holding substantial funds online—security vulnerabilities may emerge through coding errors or malicious attacks requiring continuous vigilance from developers.
3.. Competitive Landscape
Other blockchains such as Binance Smart Chain or Solana aim at offering similar functionalities with higher throughput speeds at lower costs—which could challenge Ether’s dominance if they succeed widely.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what differentiates Ethereum from Bitcoin helps investors evaluate their respective roles within broader financial ecosystems better suited either as stores of value—or innovative platforms powering decentralized services worldwide . While both projects face hurdles related to scalability security regulation—they also present tremendous opportunities driven by technological innovation shaping tomorrow’s financial landscape.
By grasping these core aspects—from fundamental purpose through recent upgrades—you can make informed decisions whether you're investing directly in ETH/BTC—or exploring how these pioneering technologies might influence your industry sector moving forward
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Could New Laws Hurt the Cryptocurrency Market?
The rapid evolution of cryptocurrency regulation has sparked widespread debate about its potential impact on the industry. As governments and regulatory bodies introduce new laws and frameworks, many investors, companies, and enthusiasts are questioning whether these changes will help foster growth or inadvertently cause harm. Understanding the current landscape is crucial to assessing how upcoming legislation might influence the future of digital assets.
The Current Regulatory Environment for Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrency's decentralized nature has always posed challenges for regulators seeking to establish clear guidelines. Unlike traditional financial systems, digital assets operate across borders with minimal oversight, raising concerns about market stability, fraud prevention, and consumer protection. The U.S., in particular, through agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), has been actively scrutinizing crypto activities—hosting roundtables and proposing regulations aimed at bringing more clarity.
However, despite efforts by authorities such as SEC Chair Paul Atkins calling for clearer rules, a significant level of regulatory uncertainty persists. This ambiguity can create hesitation among investors and businesses alike because it complicates compliance strategies and raises fears of sudden policy shifts that could devalue holdings or disrupt operations.
Recent Developments Indicating a Changing Landscape
Recent legislative proposals suggest that governments are increasingly willing to intervene more directly in crypto markets. For example:
State-Level Initiatives: New Hampshire’s move to establish a strategic Bitcoin reserve demonstrates proactive state involvement aimed at integrating cryptocurrencies into official financial strategies. Such initiatives could serve as models for other states but also signal increased government interest in controlling digital assets.
Federal Proposals: The Trump administration’s consideration of creating a government-backed Bitcoin reserve through tariffs indicates an unprecedented level of involvement—potentially setting precedents that could lead to more stringent federal regulations or even direct market manipulation.
Political Divides: While some policymakers push toward embracing cryptocurrencies with supportive policies like stablecoin promotion or strategic reserves, others express concern over market volatility and potential misuse—highlighting ongoing political disagreements that may influence future laws.
How New Laws Might Impact Cryptocurrency Markets
The introduction of new laws can have both positive and negative effects on the crypto industry:
Potential Benefits:
- Clearer regulations can legitimize cryptocurrencies in mainstream finance.
- Better consumer protections may attract institutional investors.
- State-level initiatives like Bitcoin reserves could stabilize markets by providing liquidity buffers.
Risks & Challenges:
- Market Instability: Sudden regulatory changes often lead to price swings as traders react unpredictably to news or legal uncertainties.
- Increased Compliance Costs: Stricter rules mean higher operational costs for exchanges and blockchain companies—costs which might be passed onto consumers or reduce profitability.
- Reduced Innovation: Overly restrictive legislation might stifle innovation by limiting experimentation with new blockchain applications or restricting access for startups.
- Erosion of Public Confidence: Political disagreements over regulation can undermine trust among users who fear heavy-handed oversight or government overreach.
Will Regulations Help Or Harm Cryptocurrency Growth?
While well-designed laws aim to protect investors without stifling innovation—a balance known as "regulatory sandboxes"—poorly crafted legislation risks harming growth prospects significantly. For instance:
- Excessive restrictions could drive activity underground into less transparent markets.
- Lack of clarity may deter institutional participation essential for scaling adoption.
Conversely, transparent frameworks aligned with international standards can foster sustainable growth by reducing fraud risks while encouraging responsible innovation.
What Should Stakeholders Expect Moving Forward?
Given current trends:
Expect continued debates between advocates pushing for innovation-friendly policies versus regulators prioritizing security measures.
Watch out for state-level experiments like those seen in New Hampshire—they may pave the way toward broader acceptance if successful but also risk fragmenting regulatory approaches across jurisdictions.
Companies such as Coinbase demonstrate resilience amid uncertainty; their ability to adapt will be critical in navigating evolving legal landscapes without compromising growth opportunities.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Uncertainty
The question remains whether new laws will hurt cryptocurrency markets—or if they will ultimately strengthen them by establishing legitimacy and stability. While there are legitimate concerns about increased compliance costs or reduced market freedom under stricter regulations, thoughtful policymaking rooted in transparency can mitigate these risks while fostering long-term industry health.
For investors considering exposure during this period of change—and companies planning expansion—the key lies in staying informed about legislative developments while advocating for balanced regulation that supports innovation without sacrificing security or public trust.
Keywords:cryptocurrency regulation | crypto laws impact | blockchain legal framework | crypto market stability | government involvement in crypto | SEC cryptocurrency policies | state-level crypto initiatives | future of cryptocurrency law


Lo
2025-05-11 10:16
Could new laws hurt this crypto?
Could New Laws Hurt the Cryptocurrency Market?
The rapid evolution of cryptocurrency regulation has sparked widespread debate about its potential impact on the industry. As governments and regulatory bodies introduce new laws and frameworks, many investors, companies, and enthusiasts are questioning whether these changes will help foster growth or inadvertently cause harm. Understanding the current landscape is crucial to assessing how upcoming legislation might influence the future of digital assets.
The Current Regulatory Environment for Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrency's decentralized nature has always posed challenges for regulators seeking to establish clear guidelines. Unlike traditional financial systems, digital assets operate across borders with minimal oversight, raising concerns about market stability, fraud prevention, and consumer protection. The U.S., in particular, through agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), has been actively scrutinizing crypto activities—hosting roundtables and proposing regulations aimed at bringing more clarity.
However, despite efforts by authorities such as SEC Chair Paul Atkins calling for clearer rules, a significant level of regulatory uncertainty persists. This ambiguity can create hesitation among investors and businesses alike because it complicates compliance strategies and raises fears of sudden policy shifts that could devalue holdings or disrupt operations.
Recent Developments Indicating a Changing Landscape
Recent legislative proposals suggest that governments are increasingly willing to intervene more directly in crypto markets. For example:
State-Level Initiatives: New Hampshire’s move to establish a strategic Bitcoin reserve demonstrates proactive state involvement aimed at integrating cryptocurrencies into official financial strategies. Such initiatives could serve as models for other states but also signal increased government interest in controlling digital assets.
Federal Proposals: The Trump administration’s consideration of creating a government-backed Bitcoin reserve through tariffs indicates an unprecedented level of involvement—potentially setting precedents that could lead to more stringent federal regulations or even direct market manipulation.
Political Divides: While some policymakers push toward embracing cryptocurrencies with supportive policies like stablecoin promotion or strategic reserves, others express concern over market volatility and potential misuse—highlighting ongoing political disagreements that may influence future laws.
How New Laws Might Impact Cryptocurrency Markets
The introduction of new laws can have both positive and negative effects on the crypto industry:
Potential Benefits:
- Clearer regulations can legitimize cryptocurrencies in mainstream finance.
- Better consumer protections may attract institutional investors.
- State-level initiatives like Bitcoin reserves could stabilize markets by providing liquidity buffers.
Risks & Challenges:
- Market Instability: Sudden regulatory changes often lead to price swings as traders react unpredictably to news or legal uncertainties.
- Increased Compliance Costs: Stricter rules mean higher operational costs for exchanges and blockchain companies—costs which might be passed onto consumers or reduce profitability.
- Reduced Innovation: Overly restrictive legislation might stifle innovation by limiting experimentation with new blockchain applications or restricting access for startups.
- Erosion of Public Confidence: Political disagreements over regulation can undermine trust among users who fear heavy-handed oversight or government overreach.
Will Regulations Help Or Harm Cryptocurrency Growth?
While well-designed laws aim to protect investors without stifling innovation—a balance known as "regulatory sandboxes"—poorly crafted legislation risks harming growth prospects significantly. For instance:
- Excessive restrictions could drive activity underground into less transparent markets.
- Lack of clarity may deter institutional participation essential for scaling adoption.
Conversely, transparent frameworks aligned with international standards can foster sustainable growth by reducing fraud risks while encouraging responsible innovation.
What Should Stakeholders Expect Moving Forward?
Given current trends:
Expect continued debates between advocates pushing for innovation-friendly policies versus regulators prioritizing security measures.
Watch out for state-level experiments like those seen in New Hampshire—they may pave the way toward broader acceptance if successful but also risk fragmenting regulatory approaches across jurisdictions.
Companies such as Coinbase demonstrate resilience amid uncertainty; their ability to adapt will be critical in navigating evolving legal landscapes without compromising growth opportunities.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Uncertainty
The question remains whether new laws will hurt cryptocurrency markets—or if they will ultimately strengthen them by establishing legitimacy and stability. While there are legitimate concerns about increased compliance costs or reduced market freedom under stricter regulations, thoughtful policymaking rooted in transparency can mitigate these risks while fostering long-term industry health.
For investors considering exposure during this period of change—and companies planning expansion—the key lies in staying informed about legislative developments while advocating for balanced regulation that supports innovation without sacrificing security or public trust.
Keywords:cryptocurrency regulation | crypto laws impact | blockchain legal framework | crypto market stability | government involvement in crypto | SEC cryptocurrency policies | state-level crypto initiatives | future of cryptocurrency law
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Permissioned Blockchains Differ from Permissionless?
Understanding the fundamental differences between permissioned and permissionless blockchains is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether for investment, development, or strategic planning. These two types of blockchain systems serve different purposes and are suited to various use cases based on their inherent characteristics.
What Is a Permissionless Blockchain?
A permissionless blockchain, often called a public blockchain, is an open network where anyone can participate without restrictions. This openness fosters decentralization and transparency—core principles that underpin many cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. In such networks, participants can join freely to validate transactions or develop applications like smart contracts.
The key features of permissionless blockchains include:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network; instead, control is distributed across numerous nodes worldwide.
- Open Access: Anyone with internet access can become a participant—whether as a user or validator.
- Consensus Mechanisms: They typically rely on mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to agree on transaction validity.
- Transparency: All transactions are publicly recorded on the ledger accessible by anyone.
This model was pioneering in establishing trustlessness—the idea that participants do not need to trust any central authority but rather rely on cryptographic proof and consensus protocols. Bitcoin exemplifies this approach by enabling peer-to-peer digital currency transfers without intermediaries.
Recent developments in permissionless blockchains include significant events like Bitcoin's halving scheduled for May 2024. This event reduces miners' rewards from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC per block, impacting supply dynamics and market sentiment. Ethereum’s transition from PoW to PoS (Ethereum 2.0), initiated around 2023, aims at improving scalability while reducing energy consumption—a critical step toward mainstream adoption.
What Is a Permissioned Blockchain?
In contrast, permissioned blockchains operate within closed environments where access is restricted exclusively to authorized entities. These are often used by enterprises seeking greater control over their data while leveraging blockchain benefits such as immutability and auditability.
Key characteristics include:
- Controlled Access: Only selected organizations or individuals can join the network.
- Centralized Control: Usually managed by one organization or consortium overseeing governance rules.
- Custom Consensus Protocols: They may employ tailored consensus algorithms optimized for speed and privacy rather than decentralization.
- Privacy & Confidentiality: Transactions can be private; visibility may be limited based on permissions assigned to users.
Permissioned systems are particularly suitable for industries with strict regulatory requirements—such as finance, healthcare, supply chain management—and applications where transparency needs balancing with privacy concerns. For example, IBM’s Food Trust uses a permissioned blockchain platform allowing trusted stakeholders along food supply chains to track product origins securely while maintaining confidentiality among participants.
Recent trends show increased enterprise adoption of these networks due to their ability to meet compliance standards like anti-money laundering (AML) regulations or know-your-customer (KYC) procedures prevalent in financial services sectors.
Comparing Permissionless vs Permissioned Blockchains
| Feature | Permissionless Blockchain | Permissioned Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Often centralized or semi-decentralized |
| Access | Open access | Restricted access |
| Consensus Mechanism | PoW / PoS | Custom / optimized protocols |
| Transparency | Publicly visible | Private / restricted visibility |
While both models leverage cryptography and distributed ledgers’ core principles—immutability and security—they differ significantly in scope regarding openness versus control.
Security Considerations
Permissioned blockchains tend toward higher security levels against malicious attacks because they restrict who can participate actively in validation processes; fewer nodes mean less attack surface area compared with open networks that attract more participants but also face higher risks from malicious actors attempting Sybil attacks or double-spending attempts.
However, this increased security comes at the expense of decentralization—the backbone principle behind many cryptocurrencies—which might limit resilience against systemic failures if controlling entities collude improperly or if governance structures fail.
Scalability & Adoption Challenges
Permissionless networks generally scale better due to broader participation; more validators mean faster transaction processing times under certain conditions—but they also face challenges related to throughput limitations when transaction volumes surge dramatically (e.g., Ethereum’s congestion issues). Conversely,
permissioned systems excel at high throughput owing to controlled environments but lack the global reach necessary for widespread adoption outside specific industry contexts.
Regulatory Compliance & Use Cases
One advantage of permissioned blockchains lies in their ability to comply easily with regulatory frameworks since access controls facilitate audit trails aligned with legal standards—a crucial factor for financial institutions implementing KYC/AML measures using private ledgers.
Industry Adoption Trends
Major corporations have embraced permissioned solutions: IBM's Food Trust enables transparent yet confidential tracking within food supply chains; Microsoft Azure offers enterprise-grade private blockchain platforms tailored for business needs.
Which Type Fits Your Needs?
Choosing between these two options depends heavily on your application's priorities:
If decentralization and censorship resistance are paramount—for example: cryptocurrency projects—permissionless models are preferable.
For enterprise solutions requiring privacy compliance—and where trusted parties exist—permissioned models offer better control over data sharing.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Blockchain Choices
Understanding whether your project benefits more from an open ecosystem versus controlled environment helps determine which type aligns best with your goals. While permissionless blockchains foster innovation through openness—and potentially wider adoption—they pose challenges related to scalability and regulation enforcement. Conversely,
permissioned systems provide enhanced privacy controls suited for regulated industries but sacrifice some degree of decentralization essential for trustlessness.
By evaluating these factors carefully—including recent technological advancements like Ethereum's move toward proof-of-stake mechanisms—you can make informed decisions about deploying suitable blockchain architectures aligned with your strategic objectives.
Key Dates Recap
- May 2024: Bitcoin halving event
- 2023: Transition towards Ethereum 2.0
- 2022: Launch of IBM Food Trust platform using a permissioned ledger
References
For further reading:
- "Bitcoin Halving: What You Need To Know" — CoinDesk
- "Ethereum 2.0 Transition Guide" — Coindesk
- "IBM Food Trust Uses Blockchain To Improve Supply Chain Transparency" — IBM


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 17:46
How do permissioned blockchains differ from permissionless?
How Do Permissioned Blockchains Differ from Permissionless?
Understanding the fundamental differences between permissioned and permissionless blockchains is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether for investment, development, or strategic planning. These two types of blockchain systems serve different purposes and are suited to various use cases based on their inherent characteristics.
What Is a Permissionless Blockchain?
A permissionless blockchain, often called a public blockchain, is an open network where anyone can participate without restrictions. This openness fosters decentralization and transparency—core principles that underpin many cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. In such networks, participants can join freely to validate transactions or develop applications like smart contracts.
The key features of permissionless blockchains include:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network; instead, control is distributed across numerous nodes worldwide.
- Open Access: Anyone with internet access can become a participant—whether as a user or validator.
- Consensus Mechanisms: They typically rely on mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to agree on transaction validity.
- Transparency: All transactions are publicly recorded on the ledger accessible by anyone.
This model was pioneering in establishing trustlessness—the idea that participants do not need to trust any central authority but rather rely on cryptographic proof and consensus protocols. Bitcoin exemplifies this approach by enabling peer-to-peer digital currency transfers without intermediaries.
Recent developments in permissionless blockchains include significant events like Bitcoin's halving scheduled for May 2024. This event reduces miners' rewards from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC per block, impacting supply dynamics and market sentiment. Ethereum’s transition from PoW to PoS (Ethereum 2.0), initiated around 2023, aims at improving scalability while reducing energy consumption—a critical step toward mainstream adoption.
What Is a Permissioned Blockchain?
In contrast, permissioned blockchains operate within closed environments where access is restricted exclusively to authorized entities. These are often used by enterprises seeking greater control over their data while leveraging blockchain benefits such as immutability and auditability.
Key characteristics include:
- Controlled Access: Only selected organizations or individuals can join the network.
- Centralized Control: Usually managed by one organization or consortium overseeing governance rules.
- Custom Consensus Protocols: They may employ tailored consensus algorithms optimized for speed and privacy rather than decentralization.
- Privacy & Confidentiality: Transactions can be private; visibility may be limited based on permissions assigned to users.
Permissioned systems are particularly suitable for industries with strict regulatory requirements—such as finance, healthcare, supply chain management—and applications where transparency needs balancing with privacy concerns. For example, IBM’s Food Trust uses a permissioned blockchain platform allowing trusted stakeholders along food supply chains to track product origins securely while maintaining confidentiality among participants.
Recent trends show increased enterprise adoption of these networks due to their ability to meet compliance standards like anti-money laundering (AML) regulations or know-your-customer (KYC) procedures prevalent in financial services sectors.
Comparing Permissionless vs Permissioned Blockchains
| Feature | Permissionless Blockchain | Permissioned Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Often centralized or semi-decentralized |
| Access | Open access | Restricted access |
| Consensus Mechanism | PoW / PoS | Custom / optimized protocols |
| Transparency | Publicly visible | Private / restricted visibility |
While both models leverage cryptography and distributed ledgers’ core principles—immutability and security—they differ significantly in scope regarding openness versus control.
Security Considerations
Permissioned blockchains tend toward higher security levels against malicious attacks because they restrict who can participate actively in validation processes; fewer nodes mean less attack surface area compared with open networks that attract more participants but also face higher risks from malicious actors attempting Sybil attacks or double-spending attempts.
However, this increased security comes at the expense of decentralization—the backbone principle behind many cryptocurrencies—which might limit resilience against systemic failures if controlling entities collude improperly or if governance structures fail.
Scalability & Adoption Challenges
Permissionless networks generally scale better due to broader participation; more validators mean faster transaction processing times under certain conditions—but they also face challenges related to throughput limitations when transaction volumes surge dramatically (e.g., Ethereum’s congestion issues). Conversely,
permissioned systems excel at high throughput owing to controlled environments but lack the global reach necessary for widespread adoption outside specific industry contexts.
Regulatory Compliance & Use Cases
One advantage of permissioned blockchains lies in their ability to comply easily with regulatory frameworks since access controls facilitate audit trails aligned with legal standards—a crucial factor for financial institutions implementing KYC/AML measures using private ledgers.
Industry Adoption Trends
Major corporations have embraced permissioned solutions: IBM's Food Trust enables transparent yet confidential tracking within food supply chains; Microsoft Azure offers enterprise-grade private blockchain platforms tailored for business needs.
Which Type Fits Your Needs?
Choosing between these two options depends heavily on your application's priorities:
If decentralization and censorship resistance are paramount—for example: cryptocurrency projects—permissionless models are preferable.
For enterprise solutions requiring privacy compliance—and where trusted parties exist—permissioned models offer better control over data sharing.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Blockchain Choices
Understanding whether your project benefits more from an open ecosystem versus controlled environment helps determine which type aligns best with your goals. While permissionless blockchains foster innovation through openness—and potentially wider adoption—they pose challenges related to scalability and regulation enforcement. Conversely,
permissioned systems provide enhanced privacy controls suited for regulated industries but sacrifice some degree of decentralization essential for trustlessness.
By evaluating these factors carefully—including recent technological advancements like Ethereum's move toward proof-of-stake mechanisms—you can make informed decisions about deploying suitable blockchain architectures aligned with your strategic objectives.
Key Dates Recap
- May 2024: Bitcoin halving event
- 2023: Transition towards Ethereum 2.0
- 2022: Launch of IBM Food Trust platform using a permissioned ledger
References
For further reading:
- "Bitcoin Halving: What You Need To Know" — CoinDesk
- "Ethereum 2.0 Transition Guide" — Coindesk
- "IBM Food Trust Uses Blockchain To Improve Supply Chain Transparency" — IBM
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Does SPV (Simplified Payment Verification) Work in Bitcoin?
Understanding the Basics of SPV in Bitcoin
Simplified Payment Verification (SPV) is a method that allows Bitcoin users to verify transactions without downloading and storing the entire blockchain. This approach is especially beneficial for lightweight clients like mobile wallets, which have limited storage capacity and computational resources. Unlike full nodes that maintain a complete copy of all transaction data, SPV enables users to confirm that their transactions are included in the blockchain efficiently and securely.
At its core, SPV relies on a minimal set of data—specifically, block headers—to verify transaction validity. This design significantly reduces resource requirements while maintaining a reasonable level of security for everyday use. As Bitcoin continues to grow, SPV remains an essential tool for increasing accessibility and scalability within the network.
The Mechanics Behind SPV: How It Verifies Transactions
The process begins with downloading only the block headers rather than entire blocks filled with transaction data. Each block header contains critical information such as:
- The hash of the previous block
- A timestamp
- The Merkle root (a cryptographic summary of all transactions within that block)
- Other metadata like difficulty target and nonce
This compact data structure allows clients to track the blockchain's overall state without handling every individual transaction.
To verify whether a specific transaction has been confirmed on the network, an SPV client requests a proof of inclusion from a full node—an entity that maintains complete blockchain data. This proof includes:
- The transaction ID
- A sequence of hashes forming a path through the Merkle tree from the specific transaction up to its Merkle root
Using this proof, users can perform two key checks:
- Merkle Proof Validation: Confirming that their transaction is part of the Merkle tree by reconstructing hashes along the provided path.
- Block Header Validation: Ensuring that this particular Merkle root matches one present in an accepted block header.
If both checks pass successfully, it indicates with high confidence that their transaction was included in an accepted block on the Bitcoin network.
Why Was SPV Introduced? Its Historical Context
SPV was first introduced by Greg Maxwell in 2011 as part of efforts to make Bitcoin more accessible beyond technical enthusiasts running full nodes. Prior to this innovation, verifying transactions required downloading and validating every piece of blockchain data—a process impractical for devices with limited resources like smartphones or web-based wallets.
The goal was clear: enable lightweight clients to participate securely without demanding extensive hardware capabilities or bandwidth consumption. Since then, SPV has become integral for many wallet implementations worldwide due to its simplicity and efficiency.
Security Considerations When Using SPV
While SPV offers significant advantages regarding resource efficiency and user convenience, it does come with inherent security risks worth understanding:
Susceptibility to Fake Chains: Because lightweight clients rely on external full nodes for proofs but do not independently validate all chain history fully, they could be misled if connected to malicious nodes controlling false information.
51% Attacks: If an attacker gains majority control over mining power (a 51% attack), they could potentially manipulate which blocks are considered valid or produce fraudulent proofs affecting verification accuracy.
Centralization Risks: Heavy reliance on trusted full nodes might inadvertently lead toward centralization tendencies if most users depend on few providers for validation services.
Despite these concerns, various protocol enhancements—such as better proof-of-inclusion methods—and best practices like connecting only trusted nodes help mitigate potential vulnerabilities associated with using SPV-based wallets.
Recent Advances Improving Security & Efficiency
Over recent years, developers have focused on refining how proofs are generated and verified within SPI protocols:
Enhanced Merkle Tree Structures:
- Newer algorithms optimize how hashes are combined into trees.
- These improvements reduce verification time while increasing resistance against manipulation attempts.
Better Proof Generation Methods:
- Techniques such as Compact Block Filters allow faster validation processes.
- They also minimize bandwidth usage during synchronization between peers.
Integration With Layer 2 Solutions
- Technologies like Lightning Network leverage simplified verification methods alongside traditional protocols.
- These integrations aim at scaling Bitcoin further while maintaining security standards suitable for lightweight clients.
Furthermore, ongoing research aims at developing more robust mechanisms against potential attacks targeting light client verification processes—ensuring safer participation even under adversarial conditions.
Key Milestones & Facts About SPV Development
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 2011 | Introduction of Simplified Payment Verification by Greg Maxwell |
| 2012 | Inclusion into early versions of Bitcoin Core software |
| 2013 | Identification of vulnerabilities related to fake chain attacks |
| Present | Continuous protocol improvements focusing on security enhancements |
These milestones highlight both foundational development efforts and ongoing innovations aimed at strengthening trustworthiness across different types of wallet implementations utilizing SPI techniques.
How Light Clients Benefit From Using SPI Protocols
Lightweight wallets employing SPI protocols benefit primarily through reduced storage needs—they only store minimal blockchain summaries rather than entire histories—and faster synchronization times compared with full node setups. This makes them ideal choices for mobile devices where hardware limitations restrict traditional node operation capabilities.
Limitations & Future Directions in Blockchain Verification
Despite advancements made over recent years—including improved proof structures—the reliance on external full nodes still introduces some trust assumptions not present when operating fully validating nodes independently; thus emphasizing importance around selecting reputable sources during verification processes.
Looking ahead , ongoing research focuses heavily upon enhancing decentralization aspects by enabling more secure peer-to-peer validation schemes alongside integrating new cryptographic techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs — promising even greater privacy-preserving features combined with scalable verification solutions suited specifically for future decentralized ecosystems.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how Simplified Payment Verification works provides valuable insight into making cryptocurrency networks more accessible without compromising too much security or decentralization principles . As technology evolves—with continuous protocol improvements addressing current vulnerabilities—SPV remains vital within broader efforts toward scalable adoption across diverse user bases worldwide.


JCUSER-IC8sJL1q
2025-05-09 16:37
How does SPV (Simplified Payment Verification) work in Bitcoin?
How Does SPV (Simplified Payment Verification) Work in Bitcoin?
Understanding the Basics of SPV in Bitcoin
Simplified Payment Verification (SPV) is a method that allows Bitcoin users to verify transactions without downloading and storing the entire blockchain. This approach is especially beneficial for lightweight clients like mobile wallets, which have limited storage capacity and computational resources. Unlike full nodes that maintain a complete copy of all transaction data, SPV enables users to confirm that their transactions are included in the blockchain efficiently and securely.
At its core, SPV relies on a minimal set of data—specifically, block headers—to verify transaction validity. This design significantly reduces resource requirements while maintaining a reasonable level of security for everyday use. As Bitcoin continues to grow, SPV remains an essential tool for increasing accessibility and scalability within the network.
The Mechanics Behind SPV: How It Verifies Transactions
The process begins with downloading only the block headers rather than entire blocks filled with transaction data. Each block header contains critical information such as:
- The hash of the previous block
- A timestamp
- The Merkle root (a cryptographic summary of all transactions within that block)
- Other metadata like difficulty target and nonce
This compact data structure allows clients to track the blockchain's overall state without handling every individual transaction.
To verify whether a specific transaction has been confirmed on the network, an SPV client requests a proof of inclusion from a full node—an entity that maintains complete blockchain data. This proof includes:
- The transaction ID
- A sequence of hashes forming a path through the Merkle tree from the specific transaction up to its Merkle root
Using this proof, users can perform two key checks:
- Merkle Proof Validation: Confirming that their transaction is part of the Merkle tree by reconstructing hashes along the provided path.
- Block Header Validation: Ensuring that this particular Merkle root matches one present in an accepted block header.
If both checks pass successfully, it indicates with high confidence that their transaction was included in an accepted block on the Bitcoin network.
Why Was SPV Introduced? Its Historical Context
SPV was first introduced by Greg Maxwell in 2011 as part of efforts to make Bitcoin more accessible beyond technical enthusiasts running full nodes. Prior to this innovation, verifying transactions required downloading and validating every piece of blockchain data—a process impractical for devices with limited resources like smartphones or web-based wallets.
The goal was clear: enable lightweight clients to participate securely without demanding extensive hardware capabilities or bandwidth consumption. Since then, SPV has become integral for many wallet implementations worldwide due to its simplicity and efficiency.
Security Considerations When Using SPV
While SPV offers significant advantages regarding resource efficiency and user convenience, it does come with inherent security risks worth understanding:
Susceptibility to Fake Chains: Because lightweight clients rely on external full nodes for proofs but do not independently validate all chain history fully, they could be misled if connected to malicious nodes controlling false information.
51% Attacks: If an attacker gains majority control over mining power (a 51% attack), they could potentially manipulate which blocks are considered valid or produce fraudulent proofs affecting verification accuracy.
Centralization Risks: Heavy reliance on trusted full nodes might inadvertently lead toward centralization tendencies if most users depend on few providers for validation services.
Despite these concerns, various protocol enhancements—such as better proof-of-inclusion methods—and best practices like connecting only trusted nodes help mitigate potential vulnerabilities associated with using SPV-based wallets.
Recent Advances Improving Security & Efficiency
Over recent years, developers have focused on refining how proofs are generated and verified within SPI protocols:
Enhanced Merkle Tree Structures:
- Newer algorithms optimize how hashes are combined into trees.
- These improvements reduce verification time while increasing resistance against manipulation attempts.
Better Proof Generation Methods:
- Techniques such as Compact Block Filters allow faster validation processes.
- They also minimize bandwidth usage during synchronization between peers.
Integration With Layer 2 Solutions
- Technologies like Lightning Network leverage simplified verification methods alongside traditional protocols.
- These integrations aim at scaling Bitcoin further while maintaining security standards suitable for lightweight clients.
Furthermore, ongoing research aims at developing more robust mechanisms against potential attacks targeting light client verification processes—ensuring safer participation even under adversarial conditions.
Key Milestones & Facts About SPV Development
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 2011 | Introduction of Simplified Payment Verification by Greg Maxwell |
| 2012 | Inclusion into early versions of Bitcoin Core software |
| 2013 | Identification of vulnerabilities related to fake chain attacks |
| Present | Continuous protocol improvements focusing on security enhancements |
These milestones highlight both foundational development efforts and ongoing innovations aimed at strengthening trustworthiness across different types of wallet implementations utilizing SPI techniques.
How Light Clients Benefit From Using SPI Protocols
Lightweight wallets employing SPI protocols benefit primarily through reduced storage needs—they only store minimal blockchain summaries rather than entire histories—and faster synchronization times compared with full node setups. This makes them ideal choices for mobile devices where hardware limitations restrict traditional node operation capabilities.
Limitations & Future Directions in Blockchain Verification
Despite advancements made over recent years—including improved proof structures—the reliance on external full nodes still introduces some trust assumptions not present when operating fully validating nodes independently; thus emphasizing importance around selecting reputable sources during verification processes.
Looking ahead , ongoing research focuses heavily upon enhancing decentralization aspects by enabling more secure peer-to-peer validation schemes alongside integrating new cryptographic techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs — promising even greater privacy-preserving features combined with scalable verification solutions suited specifically for future decentralized ecosystems.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how Simplified Payment Verification works provides valuable insight into making cryptocurrency networks more accessible without compromising too much security or decentralization principles . As technology evolves—with continuous protocol improvements addressing current vulnerabilities—SPV remains vital within broader efforts toward scalable adoption across diverse user bases worldwide.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Public vs. Private Blockchain: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the distinctions between public and private blockchains is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether you're an investor, developer, or business leader. Both types of blockchains leverage distributed ledger technology (DLT), but they serve different purposes and operate under different principles. This article provides a clear overview of what sets them apart, their key features, use cases, and recent trends shaping their development.
What Is a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain is an open-source network where anyone can participate without restrictions. These networks are fully decentralized—meaning no single entity controls the entire system—and rely on consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) to validate transactions. Because they are accessible to everyone globally, public blockchains promote transparency and security through widespread participation.
For example, Bitcoin was the first successful public blockchain that introduced peer-to-peer digital currency without intermediaries such as banks. Ethereum expanded on this concept by enabling smart contracts—self-executing agreements written into code—that facilitate complex decentralized applications (dApps). These platforms have fueled innovations like decentralized finance (DeFi), which allows users to lend, borrow, or trade assets directly on blockchain networks.
Public blockchains are particularly suited for applications requiring transparency and censorship resistance. Their open nature makes them ideal for financial transactions involving cryptocurrencies but also extends to supply chain tracking and voting systems where trustlessness is vital.
Characteristics of Public Blockchains
- Decentralization: Anyone can join as a node; no central authority controls the network.
- Open Access: No permission needed; anyone can read data or participate in validation.
- Transparency: All transaction data is publicly visible.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be altered retroactively.
- Security Through Consensus: Network security relies on collective agreement mechanisms like PoW or PoS.
These features foster trust among participants because they eliminate single points of failure while ensuring data integrity across all nodes.
What Is a Private Blockchain?
In contrast to public blockchains, private blockchains restrict access to authorized participants only. They are often used within organizations or consortia that require controlled environments for sharing sensitive information securely. Managed by a central authority—or sometimes by multiple trusted entities—private networks prioritize privacy and efficiency over complete decentralization.
Private blockchains enable organizations such as banks or supply chain companies to automate internal processes while maintaining strict control over who can view or modify data. For instance, Hyperledger Fabric—a popular private blockchain framework—is widely adopted in enterprise settings due to its modular architecture allowing customization according to specific compliance needs.
Because access is limited and permissions are managed centrally—or through consortium governance—private chains tend not to be fully transparent externally but offer higher throughput speeds suitable for enterprise-scale operations requiring confidentiality.
Key Features of Private Blockchains
- Controlled Access: Only selected users with permissions can join the network.
- Closed Source/Permissioned: The codebase may not be publicly available; modifications are controlled.
- Data Privacy: Transaction details are visible only among authorized parties.
- Higher Performance & Scalability: Reduced consensus overhead leads to faster transaction processing.
- Governance & Compliance Focused: Designed with regulatory requirements in mind—for example GDPR compliance in Europe.
This structure makes private blockchains attractive for industries needing secure yet confidential recordkeeping without exposing sensitive information externally.
Comparing Public vs Private Blockchains
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Open worldwide | Restricted membership |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Partially centralized |
| Transparency | Complete visibility | Limited visibility |
| Speed & Scalability | Lower due to consensus complexity | Higher performance |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies; DeFi; voting systems | Internal processes; supply chains; compliance |
While both types aim at enhancing security through cryptography and distributed ledgers, their design choices reflect differing priorities: openness versus control depending on application needs.
Recent Trends & Developments
The landscape of blockchain continues evolving rapidly:
Enterprise Adoption: Many corporations prefer private chains like Hyperledger Fabric because they align with regulatory standards while offering scalability benefits necessary for large-scale operations such as banking transactions or healthcare records management.
Hybrid Models: Some projects combine elements from both worlds—public permissioned chains—to balance transparency with privacy concerns effectively—a trend gaining traction especially within regulated sectors like finance and government services.
Regulatory Environment: As governments scrutinize cryptocurrencies more closely—with notable figures such as SEC Chair Paul Atkins emphasizing oversight—the distinction between public tokens versus permissioned networks becomes increasingly significant from legal perspectives.
Security Considerations: While both models provide high levels of cryptographic security when properly implemented, private networks face risks related mainly to insider threats if governance isn’t robust enough.
Technological Innovations: Advances include interoperability solutions allowing seamless communication between different types of ledgers—a step toward integrated multi-chain ecosystems supporting diverse organizational needs.
Understanding these developments helps stakeholders make informed decisions about deploying appropriate blockchain solutions aligned with strategic goals and compliance requirements.
Which Type Fits Your Needs?
Choosing between a public versus private blockchain depends heavily on your specific objectives:
If your priority is transparency —such as tracking product provenance across global supply chains—or creating open financial ecosystems—public chains might be best suited—you should consider factors like scalability limitations due to consensus protocols though these remain areas under active research improving performance metrics over time.
Conversely if your organization handles sensitive customer data requiring strict confidentiality—and you need faster transaction speeds—a private chain offers better control over access rights while still leveraging core DLT benefits.
Ultimately understanding these differences enables better alignment with industry standards—including E-A-T principles—to ensure trustworthy implementation that meets user expectations regarding security expertise and authoritative practices.
Final Thoughts
The debate between public versus private blockchains centers around balancing openness against control based on application demands—from democratized cryptocurrency markets favoring decentralization towards highly regulated industries prioritizing privacy/security measures respectively.. As technological innovations continue pushing boundaries—including interoperability protocols—the lines may blur further creating hybrid models tailored precisely per organizational needs.
Staying informed about recent trends ensures stakeholders harness blockchain's full potential responsibly while adhering best practices rooted in transparency—and building trust among users across various sectors seeking reliable digital transformation tools today


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-05-09 12:19
What is the difference between a public and a private blockchain?
Public vs. Private Blockchain: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the distinctions between public and private blockchains is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology, whether you're an investor, developer, or business leader. Both types of blockchains leverage distributed ledger technology (DLT), but they serve different purposes and operate under different principles. This article provides a clear overview of what sets them apart, their key features, use cases, and recent trends shaping their development.
What Is a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain is an open-source network where anyone can participate without restrictions. These networks are fully decentralized—meaning no single entity controls the entire system—and rely on consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) to validate transactions. Because they are accessible to everyone globally, public blockchains promote transparency and security through widespread participation.
For example, Bitcoin was the first successful public blockchain that introduced peer-to-peer digital currency without intermediaries such as banks. Ethereum expanded on this concept by enabling smart contracts—self-executing agreements written into code—that facilitate complex decentralized applications (dApps). These platforms have fueled innovations like decentralized finance (DeFi), which allows users to lend, borrow, or trade assets directly on blockchain networks.
Public blockchains are particularly suited for applications requiring transparency and censorship resistance. Their open nature makes them ideal for financial transactions involving cryptocurrencies but also extends to supply chain tracking and voting systems where trustlessness is vital.
Characteristics of Public Blockchains
- Decentralization: Anyone can join as a node; no central authority controls the network.
- Open Access: No permission needed; anyone can read data or participate in validation.
- Transparency: All transaction data is publicly visible.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be altered retroactively.
- Security Through Consensus: Network security relies on collective agreement mechanisms like PoW or PoS.
These features foster trust among participants because they eliminate single points of failure while ensuring data integrity across all nodes.
What Is a Private Blockchain?
In contrast to public blockchains, private blockchains restrict access to authorized participants only. They are often used within organizations or consortia that require controlled environments for sharing sensitive information securely. Managed by a central authority—or sometimes by multiple trusted entities—private networks prioritize privacy and efficiency over complete decentralization.
Private blockchains enable organizations such as banks or supply chain companies to automate internal processes while maintaining strict control over who can view or modify data. For instance, Hyperledger Fabric—a popular private blockchain framework—is widely adopted in enterprise settings due to its modular architecture allowing customization according to specific compliance needs.
Because access is limited and permissions are managed centrally—or through consortium governance—private chains tend not to be fully transparent externally but offer higher throughput speeds suitable for enterprise-scale operations requiring confidentiality.
Key Features of Private Blockchains
- Controlled Access: Only selected users with permissions can join the network.
- Closed Source/Permissioned: The codebase may not be publicly available; modifications are controlled.
- Data Privacy: Transaction details are visible only among authorized parties.
- Higher Performance & Scalability: Reduced consensus overhead leads to faster transaction processing.
- Governance & Compliance Focused: Designed with regulatory requirements in mind—for example GDPR compliance in Europe.
This structure makes private blockchains attractive for industries needing secure yet confidential recordkeeping without exposing sensitive information externally.
Comparing Public vs Private Blockchains
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Open worldwide | Restricted membership |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Partially centralized |
| Transparency | Complete visibility | Limited visibility |
| Speed & Scalability | Lower due to consensus complexity | Higher performance |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies; DeFi; voting systems | Internal processes; supply chains; compliance |
While both types aim at enhancing security through cryptography and distributed ledgers, their design choices reflect differing priorities: openness versus control depending on application needs.
Recent Trends & Developments
The landscape of blockchain continues evolving rapidly:
Enterprise Adoption: Many corporations prefer private chains like Hyperledger Fabric because they align with regulatory standards while offering scalability benefits necessary for large-scale operations such as banking transactions or healthcare records management.
Hybrid Models: Some projects combine elements from both worlds—public permissioned chains—to balance transparency with privacy concerns effectively—a trend gaining traction especially within regulated sectors like finance and government services.
Regulatory Environment: As governments scrutinize cryptocurrencies more closely—with notable figures such as SEC Chair Paul Atkins emphasizing oversight—the distinction between public tokens versus permissioned networks becomes increasingly significant from legal perspectives.
Security Considerations: While both models provide high levels of cryptographic security when properly implemented, private networks face risks related mainly to insider threats if governance isn’t robust enough.
Technological Innovations: Advances include interoperability solutions allowing seamless communication between different types of ledgers—a step toward integrated multi-chain ecosystems supporting diverse organizational needs.
Understanding these developments helps stakeholders make informed decisions about deploying appropriate blockchain solutions aligned with strategic goals and compliance requirements.
Which Type Fits Your Needs?
Choosing between a public versus private blockchain depends heavily on your specific objectives:
If your priority is transparency —such as tracking product provenance across global supply chains—or creating open financial ecosystems—public chains might be best suited—you should consider factors like scalability limitations due to consensus protocols though these remain areas under active research improving performance metrics over time.
Conversely if your organization handles sensitive customer data requiring strict confidentiality—and you need faster transaction speeds—a private chain offers better control over access rights while still leveraging core DLT benefits.
Ultimately understanding these differences enables better alignment with industry standards—including E-A-T principles—to ensure trustworthy implementation that meets user expectations regarding security expertise and authoritative practices.
Final Thoughts
The debate between public versus private blockchains centers around balancing openness against control based on application demands—from democratized cryptocurrency markets favoring decentralization towards highly regulated industries prioritizing privacy/security measures respectively.. As technological innovations continue pushing boundaries—including interoperability protocols—the lines may blur further creating hybrid models tailored precisely per organizational needs.
Staying informed about recent trends ensures stakeholders harness blockchain's full potential responsibly while adhering best practices rooted in transparency—and building trust among users across various sectors seeking reliable digital transformation tools today
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
🚨 Announcement on Abnormal Application Data of Mini IPO AJE Project
Due to the abnormal application data of the AJE project in the Mini IPO section, we have received feedback from multiple community users that the AJE project application has been unable to complete the withdrawal operation for several consecutive days. The platform attaches great importance to the safety of user assets, has initiated a risk control mechanism, suspended trading at the request of the project party, verified the situation with the AJE team, and assisted the project team in completing the data verification work.
👉 Details: https://support.jucoin.blog/hc/en-001/articles/49548798192025?utm_campaign=relisting_AJE&utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=post


JuCoin Official
2025-08-06 08:12
🚨 Announcement on Abnormal Application Data of Mini IPO AJE Project
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
JuCoin is pleased to announce the launch of xStocks Spot Trading (Phase 4 on Aug. 4, 2025. We welcome all users to participate in trading. Below are the details:
🔹Trading Pairs: ABBVX/USDT、ACNX/USDT、AZNX/USDT、CMCSAX/USDT、CRWDX/USDT、HDX/USDT、KOX/USDT、NFLXX/USDT、PEPX/USDT、PGX/USDT、UNHX/USDT、VTIX/USDT
🔹Trading Time: Aug. 4, 2025 at 07:00 (UTC)
👉 More: https://bit.ly/3U8VIYP



JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 04:34
🚨 xStocks Spot Trading Zone (Phase 4)
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
📅 August 4 2025
🎉 Stay updated with the latest crypto market trends!
👉 Trade on:https://bit.ly/3DFYq30
👉 X:https://twitter.com/Jucoinex
👉 APP download: https://www.jucoin.com/en/community-downloads
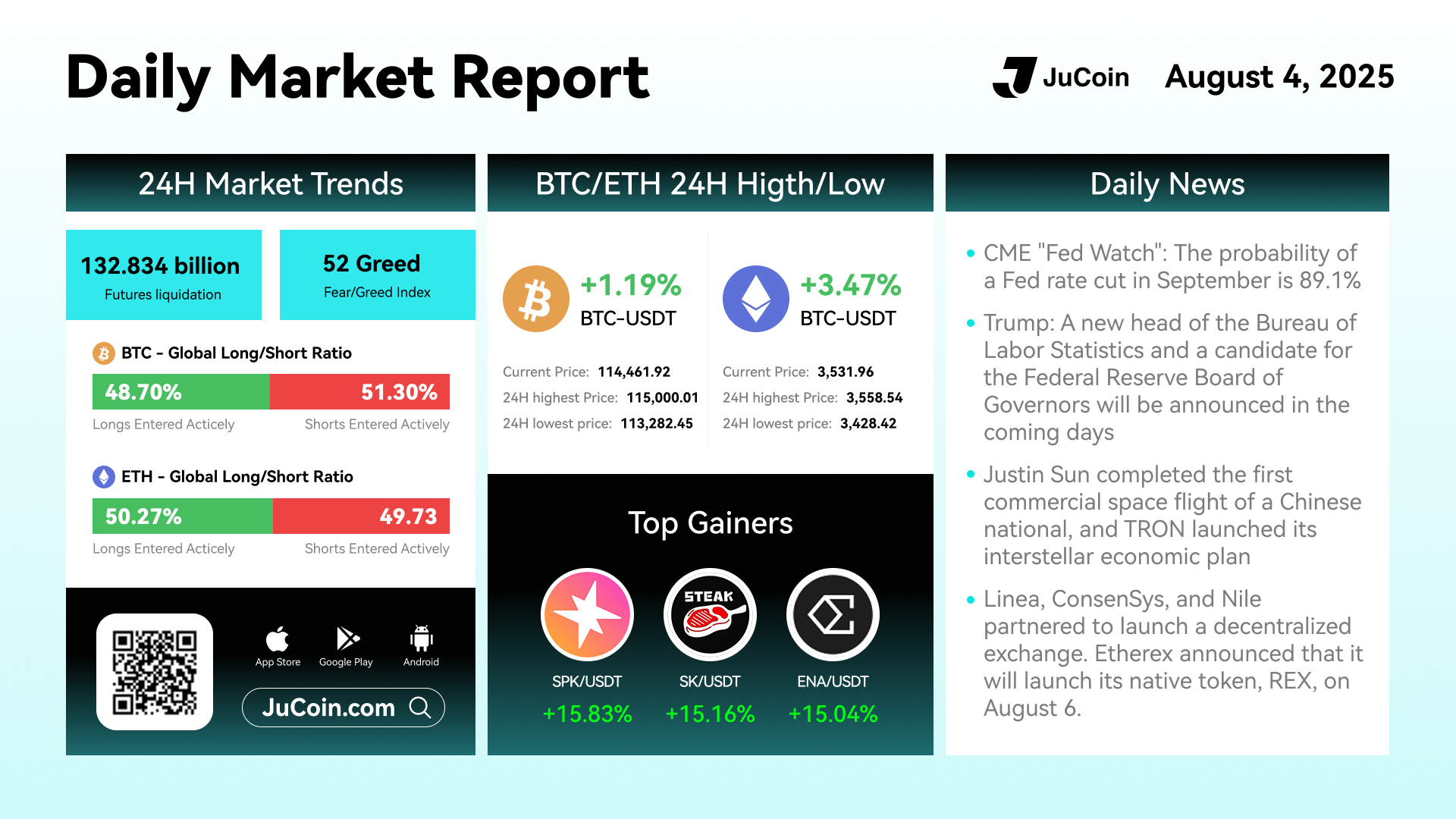


JuCoin Community
2025-08-04 04:34
🚀 #JuCoin Daily Market Report
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
TA used to be charts, indicators, and KD lines 🎯 Now it’s just tweets, vibes, and memes 🫥 Accurate enough, right?
Check out our YouTube Channel 👉
#TechnicalAnalysis #MemeTrading #CryptoTA


JuCoin Media
2025-08-01 11:35
Technical Analysis Cryptocurrency 📊 | The Only Chart That Matters
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
📅 July 31 2025
🎉 Stay updated with the latest crypto market trends!
👉 Trade on:https://bit.ly/3DFYq30
👉 X:https://twitter.com/Jucoinex
👉 APP download: https://www.jucoin.com/en/community-downloads
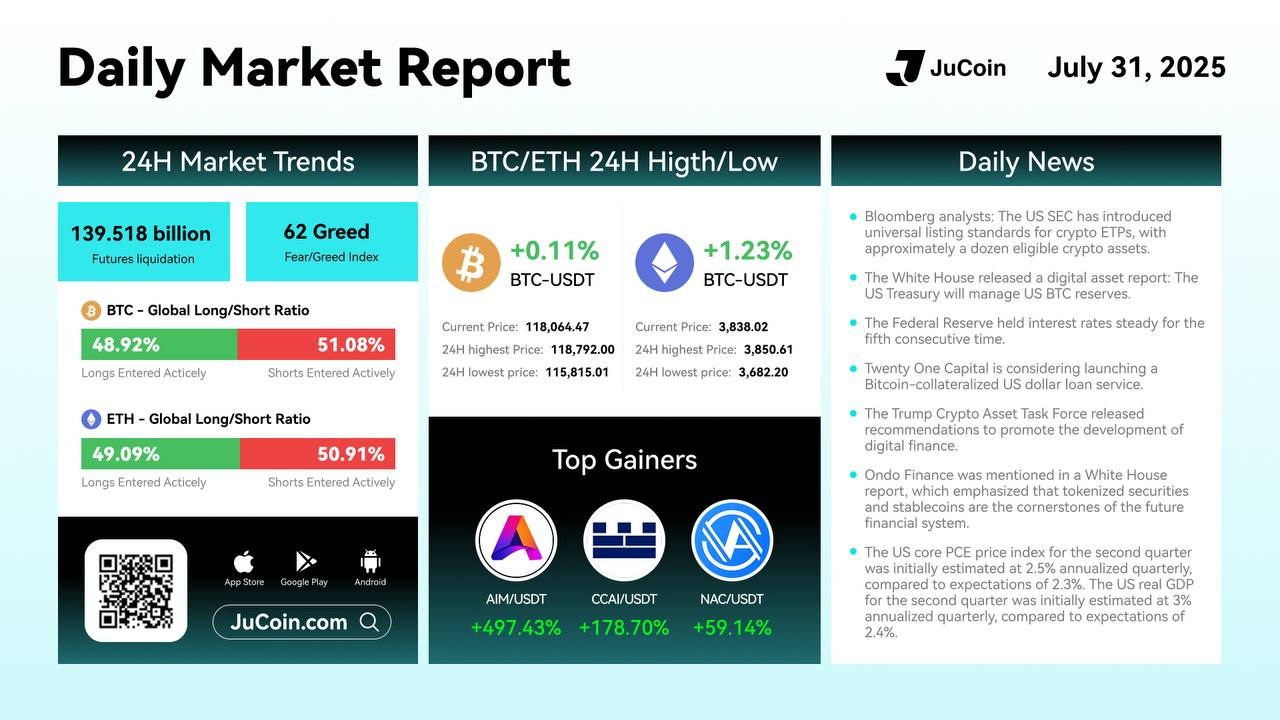


JuCoin Community
2025-07-31 06:30
🚀 #JuCoin Daily Market Report
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
👌 Your on-chain assets are your identity rights! Through an innovative "hashrate" mechanism, we convert your wallet assets (tokens/NFTs/contract actions) into equity credentials. Open the JuCoin Web3 wallet to create or import a wallet, automatically identify your computing power level, and claim JU rewards daily!
Based on your crypto asset holdings, you can earn JU computing power rewards worth up to 110 USDT!
💰 Bonus Rewards: Hold 100+ $JU tokens 20 USDT Hold ETH 10th Anniversary NFT 30 USDT
Open your JuCoin Web3 Wallet now to check your hashrate tier, secure your identity early, and position yourself for the upcoming NFT marketplace!
JuCoin Wallet Download:https://wallet.jucoin.com/en/download?utm_campaign=eth10&utm_source=telegram&utm_medium=post
Ethereum 10th Anniversary NFT Mint:https://ethereum.org/en/10years/



JuCoin Community
2025-07-31 06:29
🔹 Special Ethereum 10th Anniversary Gift! JuCoin Launches JuPower Hashrate Airdrop Plan
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
💚10 new spot listings added
💚9 campaigns launched this week
💚Platform token $JU surged over 4.68%
Stay connected with JuCoin and never miss an update!
👉 Register Now:https://www.jucoin.online/en/accounts/register?ref=MR6KTR
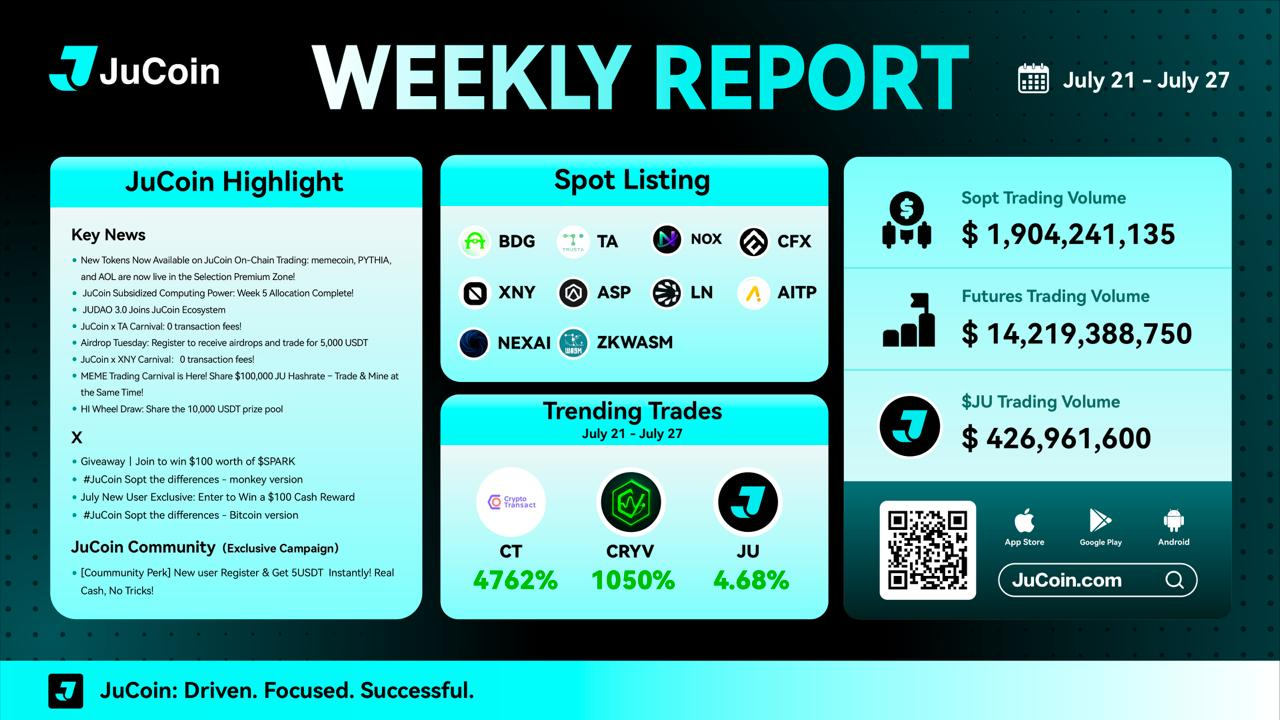


JuCoin Community
2025-07-31 06:26
JuCoin Weekly Report | July 21 – July 27 🔥
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Does OKX Pay Differ from Traditional Payment Methods?
Understanding the key differences between emerging digital payment solutions like OKX Pay and traditional payment methods is essential for users navigating the evolving financial landscape. As cryptocurrencies gain mainstream acceptance, platforms such as OKX Pay are reshaping how transactions are conducted, offering distinct advantages and unique features that set them apart from conventional systems.
What Is OKX Pay?
OKX Pay is a digital payment platform developed by OKX, one of the world's leading cryptocurrency exchanges. Unlike traditional banking or card-based payments, OKX Pay enables users to buy, sell, and manage cryptocurrencies directly within its ecosystem. It supports seamless fiat-to-crypto conversions using various currencies like USD and EUR, allowing users to fund their accounts quickly without relying on intermediaries such as banks or third-party services.
This service caters to both novice investors and experienced traders by providing an intuitive interface coupled with robust security measures. Its global accessibility ensures that users across different regions can participate in cryptocurrency markets efficiently.
Key Features of OKX Pay
- Direct Fiat-to-Crypto Transactions: Users can convert fiat currencies into popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH) instantly.
- User-Friendly Interface: Designed for ease of use regardless of experience level.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Incorporates multi-signature wallets and advanced encryption protocols to safeguard user assets.
- Global Reach: Available worldwide, facilitating cross-border transactions without geographical restrictions.
How Does It Compare with Traditional Payment Methods?
Speed of Transactions
Traditional payments through banks or credit cards often involve multiple intermediaries—such as clearinghouses—that can delay transaction processing from hours up to several days. In contrast, OKX Pay leverages blockchain technology for direct transfers that significantly reduce processing times. This immediacy benefits both individual consumers making quick purchases and institutional traders executing large trades swiftly.
Fees and Charges
Conventional payment channels typically impose higher fees due to intermediary costs—ranging from transaction fees on bank transfers to currency conversion charges on credit cards. Conversely, digital platforms like OKX Pay tend to offer more transparent fee structures with lower costs overall. Many transactions are processed at minimal or no additional charges beyond network fees, making it a cost-effective alternative especially for frequent traders.
Accessibility Across Borders
While traditional banking services may be limited by regional restrictions—requiring extensive documentation or facing currency exchange hurdles—OKX Pay's global infrastructure allows anyone with internet access to participate in crypto markets regardless of location. This democratization opens opportunities for unbanked populations or those in countries with restrictive financial systems.
Security Considerations
Although conventional payment methods have established security protocols—including fraud detection systems—the rise of digital currencies introduces new challenges such as cyber threats targeting private keys or phishing scams. Platforms like OKX address these concerns through multi-layered security features tailored specifically for crypto assets — including encrypted wallets and multi-signature authorization processes — enhancing user confidence in their transactions.
Recent Developments Enhancing Differentiation
The evolution of platforms like OKX has seen significant advancements aimed at bridging gaps between traditional finance and decentralized ecosystems:
- Integration with DeFi Platforms: Users can leverage their balances within decentralized finance applications—for lending, borrowing—and diversify investment strategies beyond simple trading.
- Expansion of Supported Currencies: Increasingly broad support for various fiat currencies alongside numerous cryptocurrencies enhances flexibility.
- Regulatory Compliance: Strict adherence to AML (Anti-Money Laundering) standards ensures legitimacy while fostering trust among institutional investors—a critical factor differentiating reputable crypto services from less regulated counterparts.
Implications for Users Moving Forward
As regulatory landscapes evolve globally around cryptocurrency usage—and market volatility remains inherent—the role of platforms like OKX becomes even more pivotal in shaping future financial interactions:
- Increased scrutiny may lead to tighter compliance requirements but also greater legitimacy.
- Market fluctuations necessitate cautious management; holding assets via secure wallets reduces exposure risks.
- Continuous innovation aims at improving user experience while maintaining high-security standards—a vital aspect aligning with best practices recognized by industry experts.
Potential Challenges Facing Digital Payment Systems Like OKX Pay
Despite its advantages over traditional methods, adopting solutions such as OKX comes with considerations:
Regulatory Risks: Governments worldwide are developing frameworks specific to crypto payments which could impact operational models or impose restrictions impacting accessibility.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices fluctuate rapidly; holding funds within these platforms exposes users directly to market swings affecting asset value stability over short periods.
Cybersecurity Threats: While robust measures exist against hacking attempts—users must remain vigilant against phishing attacks targeting login credentials or private keys.
Embracing the Future: How Digital Payments Are Changing Financial Transactions
The shift towards digital-first approaches exemplified by platforms like OK X signifies a broader transformation in how individuals conduct financial activities globally . Faster settlement times combined with lower costs make them attractive options not only for seasoned traders but also everyday consumers seeking efficient ways to manage money across borders .
By integrating seamlessly into decentralized finance ecosystems while adhering strictlyto regulatory standards , these innovations foster increased trustworthiness . As adoption grows alongside technological improvements , understanding these distinctions helps consumers make informed decisions alignedwith their needsand risk appetite .
In summary ,OK XPay’s approach offers notable advantages over conventional methods—including speed , cost-efficiency , accessibility ,and enhanced security —while also presenting new challenges linkedto regulationand market volatility . Recognizing these factors equips users better positionedto navigate this dynamic landscape effectively .


JCUSER-WVMdslBw
2025-06-11 16:23
How does OKX Pay differ from traditional payment methods?
How Does OKX Pay Differ from Traditional Payment Methods?
Understanding the key differences between emerging digital payment solutions like OKX Pay and traditional payment methods is essential for users navigating the evolving financial landscape. As cryptocurrencies gain mainstream acceptance, platforms such as OKX Pay are reshaping how transactions are conducted, offering distinct advantages and unique features that set them apart from conventional systems.
What Is OKX Pay?
OKX Pay is a digital payment platform developed by OKX, one of the world's leading cryptocurrency exchanges. Unlike traditional banking or card-based payments, OKX Pay enables users to buy, sell, and manage cryptocurrencies directly within its ecosystem. It supports seamless fiat-to-crypto conversions using various currencies like USD and EUR, allowing users to fund their accounts quickly without relying on intermediaries such as banks or third-party services.
This service caters to both novice investors and experienced traders by providing an intuitive interface coupled with robust security measures. Its global accessibility ensures that users across different regions can participate in cryptocurrency markets efficiently.
Key Features of OKX Pay
- Direct Fiat-to-Crypto Transactions: Users can convert fiat currencies into popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH) instantly.
- User-Friendly Interface: Designed for ease of use regardless of experience level.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Incorporates multi-signature wallets and advanced encryption protocols to safeguard user assets.
- Global Reach: Available worldwide, facilitating cross-border transactions without geographical restrictions.
How Does It Compare with Traditional Payment Methods?
Speed of Transactions
Traditional payments through banks or credit cards often involve multiple intermediaries—such as clearinghouses—that can delay transaction processing from hours up to several days. In contrast, OKX Pay leverages blockchain technology for direct transfers that significantly reduce processing times. This immediacy benefits both individual consumers making quick purchases and institutional traders executing large trades swiftly.
Fees and Charges
Conventional payment channels typically impose higher fees due to intermediary costs—ranging from transaction fees on bank transfers to currency conversion charges on credit cards. Conversely, digital platforms like OKX Pay tend to offer more transparent fee structures with lower costs overall. Many transactions are processed at minimal or no additional charges beyond network fees, making it a cost-effective alternative especially for frequent traders.
Accessibility Across Borders
While traditional banking services may be limited by regional restrictions—requiring extensive documentation or facing currency exchange hurdles—OKX Pay's global infrastructure allows anyone with internet access to participate in crypto markets regardless of location. This democratization opens opportunities for unbanked populations or those in countries with restrictive financial systems.
Security Considerations
Although conventional payment methods have established security protocols—including fraud detection systems—the rise of digital currencies introduces new challenges such as cyber threats targeting private keys or phishing scams. Platforms like OKX address these concerns through multi-layered security features tailored specifically for crypto assets — including encrypted wallets and multi-signature authorization processes — enhancing user confidence in their transactions.
Recent Developments Enhancing Differentiation
The evolution of platforms like OKX has seen significant advancements aimed at bridging gaps between traditional finance and decentralized ecosystems:
- Integration with DeFi Platforms: Users can leverage their balances within decentralized finance applications—for lending, borrowing—and diversify investment strategies beyond simple trading.
- Expansion of Supported Currencies: Increasingly broad support for various fiat currencies alongside numerous cryptocurrencies enhances flexibility.
- Regulatory Compliance: Strict adherence to AML (Anti-Money Laundering) standards ensures legitimacy while fostering trust among institutional investors—a critical factor differentiating reputable crypto services from less regulated counterparts.
Implications for Users Moving Forward
As regulatory landscapes evolve globally around cryptocurrency usage—and market volatility remains inherent—the role of platforms like OKX becomes even more pivotal in shaping future financial interactions:
- Increased scrutiny may lead to tighter compliance requirements but also greater legitimacy.
- Market fluctuations necessitate cautious management; holding assets via secure wallets reduces exposure risks.
- Continuous innovation aims at improving user experience while maintaining high-security standards—a vital aspect aligning with best practices recognized by industry experts.
Potential Challenges Facing Digital Payment Systems Like OKX Pay
Despite its advantages over traditional methods, adopting solutions such as OKX comes with considerations:
Regulatory Risks: Governments worldwide are developing frameworks specific to crypto payments which could impact operational models or impose restrictions impacting accessibility.
Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices fluctuate rapidly; holding funds within these platforms exposes users directly to market swings affecting asset value stability over short periods.
Cybersecurity Threats: While robust measures exist against hacking attempts—users must remain vigilant against phishing attacks targeting login credentials or private keys.
Embracing the Future: How Digital Payments Are Changing Financial Transactions
The shift towards digital-first approaches exemplified by platforms like OK X signifies a broader transformation in how individuals conduct financial activities globally . Faster settlement times combined with lower costs make them attractive options not only for seasoned traders but also everyday consumers seeking efficient ways to manage money across borders .
By integrating seamlessly into decentralized finance ecosystems while adhering strictlyto regulatory standards , these innovations foster increased trustworthiness . As adoption grows alongside technological improvements , understanding these distinctions helps consumers make informed decisions alignedwith their needsand risk appetite .
In summary ,OK XPay’s approach offers notable advantages over conventional methods—including speed , cost-efficiency , accessibility ,and enhanced security —while also presenting new challenges linkedto regulationand market volatility . Recognizing these factors equips users better positionedto navigate this dynamic landscape effectively .
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Do Credit Spreads Compare to Other Investment Strategies?
Understanding the role of credit spreads in investment decision-making is essential for investors seeking to optimize their portfolios. While credit spreads are a key indicator within fixed-income markets, they are often compared with other strategies such as equity investing, diversification techniques, and alternative assets. This article explores how credit spread-based strategies stack up against other approaches, providing clarity on their advantages and limitations.
What Are Credit Spread Strategies?
Credit spread strategies involve analyzing the difference in yields between bonds of similar credit quality but different maturities or risk profiles. Investors leverage this information to identify opportunities for higher returns or risk mitigation. For example, buying high-yield bonds when spreads are wide can offer attractive income potential if market conditions improve. Conversely, narrowing spreads might signal a safer environment suitable for more conservative investments.
These strategies are rooted in market sentiment and economic outlooks; widening spreads often indicate increased default risk or economic downturns, while narrowing spreads suggest confidence and stability. As such, credit spread analysis provides real-time insights into market health that can inform tactical investment decisions.
Comparing Credit Spreads with Equity Investment Strategies
Equity investing focuses on purchasing shares of companies with growth potential or dividend income. Unlike fixed-income securities where returns depend largely on interest rates and credit risk perceptions (reflected through credit spreads), equities are driven by company performance, earnings growth, and broader economic factors.
While both approaches aim for capital appreciation or income generation:
- Risk Profile: Equities tend to be more volatile than bonds; however, they also offer higher return potential over the long term.
- Market Sensitivity: Equity prices react sharply to corporate news and macroeconomic shifts; bond markets respond primarily through changes in interest rates and credit conditions.
- Diversification Benefits: Combining equities with fixed-income instruments like bonds can reduce overall portfolio volatility—credit spreads help gauge when bond markets may be more attractive relative to stocks.
In essence, while equity strategies focus on company fundamentals and growth prospects, credit spread-based bond strategies provide insight into macroeconomic risks that influence debt markets.
How Do Credit Spread Strategies Compare With Diversification Techniques?
Diversification is a fundamental principle across all investment styles—spreading investments across asset classes reduces exposure to any single source of risk. Using credit spreads as part of a diversification strategy involves adjusting bond holdings based on perceived risks indicated by spread movements.
For example:
- When credit spreads widen significantly due to economic uncertainty or rising default fears, an investor might reduce exposure to high-yield bonds.
- Conversely, narrowing spreads could signal an opportunity to increase allocations toward corporate debt for better yield prospects without taking excessive additional risk.
Compared with broad diversification across stocks and commodities alone,
- Credit Spread Analysis Offers Tactical Edge: It allows investors to fine-tune their fixed-income allocations based on current market signals.
- Limitations: Relying solely on spread movements without considering other factors like macroeconomic data may lead to misjudgments during volatile periods when signals become noisy.
Thus, integrating credit spread analysis enhances traditional diversification by adding a layer of tactical insight specific to bond markets' dynamics.
Comparing Credit Spreads With Alternative Asset Classes
Alternative investments include real estate (REITs), commodities (gold), hedge funds, private equity—and increasingly cryptocurrencies. These assets often serve as hedges against inflation or sources of uncorrelated returns but come with distinct risks compared to traditional bonds influenced by credit spreads.
For instance:
- Cryptocurrencies have shown high volatility unrelated directly to traditional financial indicators like interest rates or default risks reflected in bond yields.
- Real estate investments tend not directly tied but can be affected indirectly through broader economic conditions impacting borrowing costs signaled via widening or narrowing credits spreds.
Investors comparing these options should consider:
- The liquidity profile
- Risk-return characteristics
- Correlation patterns during different economic cycles
While alternative assets diversify away from fixed-income risks indicated by changing credits spreds—they do not replace the predictive power that analyzing these spreds offers regarding macroeconomic health.
Strengths & Limitations of Using Credit Spreads Compared To Other Strategies
Credit-spread-based investing provides valuable insights into market sentiment about default risk which is crucial during periods of economic stress—such as recessions—or rapid rate hikes by central banks[1]. Its strength lies in its abilityto act as an early warning system for deteriorating financial conditions before they fully materialize in stock prices or GDP figures[2].
However,
Strengths:
– Provides timely signals about systemic risks– Enhances tactical asset allocation decisions– Helps identify undervalued debt securities during turbulent times
Limitations:
– Can be misleading if used without considering macroeconomic context– Sensitive to liquidity shocks affecting bond markets disproportionately– Not always predictive during unprecedented events like pandemics
Compared with passive buy-and-hold equity approaches—which rely heavily on long-term fundamentals—credit-spread trading demands active management skills but offers potentially higher short-term gains if executed correctly.
Integrating Multiple Approaches for Better Portfolio Management
The most effective investment portfolios typically combine multiple strategies tailored accordingto individual goalsandrisk tolerance.[3] Incorporating insights fromcreditspread analysis alongside equity valuation modelsand diversifications techniques creates a balanced approach capableof navigating varyingmarket environments effectively.[4]
For example,
- Usecreditspread trendsas partof your macroeconomic outlook assessment,
- Combine thiswith fundamental analysisof individual stocks,
- Maintain diversified holdingsacross asset classes including equities,reits,and commodities,
- Adjust allocations dynamically basedon evolving signalsfrom all sources,
This integrated approach leverages each strategy's strengths while mitigating weaknesses inherentin any single method.
Final Thoughts: Choosing Between Different Investment Approaches
When evaluating whether tousecredit-spread-basedstrategies versus others,it’s importantto consider yourinvestment horizon,timeframe,andrisk appetite.[5] Fixed-income tactics centered around monitoringcreditspreds excel at capturing short-to-medium-term shiftsin market sentimentanddefault expectations,but may underperformduring prolonged bull runsor whenmacro indicators diverge frombond-market signals.[6]
Meanwhile,equity-focusedinvestmentsoffergrowthpotentialbutcomewithhighervolatilityand longer recovery periodsafter downturns.[7] Diversification remains key—blending multiple methods ensures resilienceagainst unpredictablemarket shockswhile aligningwith personalfinancial goals.[8]
By understanding how each approach compares—and recognizingthe unique advantagesofferedbycredit-spread analysis—youcan crafta well-informedstrategy suitedtothe currentmarket landscape.
References
[1] Smith J., "The Role Of Credit Spreads In Economic Forecasting," Journal Of Financial Markets 2022
[2] Lee A., "Market Sentiment Indicators And Their Predictive Power," Financial Analysts Journal 2023
[3] Brown P., "Portfolio Diversification Techniques," Investopedia 2020
[4] Johnson M., "Combining Asset Allocation Models," CFA Institute Publications 2021
[5] Davis R., "Investment Time Horizons And Strategy Selection," Harvard Business Review 2019
[6] Patel S., "Risks Of Fixed Income Investing During Economic Cycles," Bloomberg Markets 2020
[7] Nguyen T., "Equity vs Bond Investing During Market Volatility," Wall Street Journal 2021
[8] Carter L., "Building Resilient Portfolios Through Multi-Asset Strategies," Financial Times 2022


Lo
2025-06-09 22:25
How do credit spreads compare to other investment strategies?
How Do Credit Spreads Compare to Other Investment Strategies?
Understanding the role of credit spreads in investment decision-making is essential for investors seeking to optimize their portfolios. While credit spreads are a key indicator within fixed-income markets, they are often compared with other strategies such as equity investing, diversification techniques, and alternative assets. This article explores how credit spread-based strategies stack up against other approaches, providing clarity on their advantages and limitations.
What Are Credit Spread Strategies?
Credit spread strategies involve analyzing the difference in yields between bonds of similar credit quality but different maturities or risk profiles. Investors leverage this information to identify opportunities for higher returns or risk mitigation. For example, buying high-yield bonds when spreads are wide can offer attractive income potential if market conditions improve. Conversely, narrowing spreads might signal a safer environment suitable for more conservative investments.
These strategies are rooted in market sentiment and economic outlooks; widening spreads often indicate increased default risk or economic downturns, while narrowing spreads suggest confidence and stability. As such, credit spread analysis provides real-time insights into market health that can inform tactical investment decisions.
Comparing Credit Spreads with Equity Investment Strategies
Equity investing focuses on purchasing shares of companies with growth potential or dividend income. Unlike fixed-income securities where returns depend largely on interest rates and credit risk perceptions (reflected through credit spreads), equities are driven by company performance, earnings growth, and broader economic factors.
While both approaches aim for capital appreciation or income generation:
- Risk Profile: Equities tend to be more volatile than bonds; however, they also offer higher return potential over the long term.
- Market Sensitivity: Equity prices react sharply to corporate news and macroeconomic shifts; bond markets respond primarily through changes in interest rates and credit conditions.
- Diversification Benefits: Combining equities with fixed-income instruments like bonds can reduce overall portfolio volatility—credit spreads help gauge when bond markets may be more attractive relative to stocks.
In essence, while equity strategies focus on company fundamentals and growth prospects, credit spread-based bond strategies provide insight into macroeconomic risks that influence debt markets.
How Do Credit Spread Strategies Compare With Diversification Techniques?
Diversification is a fundamental principle across all investment styles—spreading investments across asset classes reduces exposure to any single source of risk. Using credit spreads as part of a diversification strategy involves adjusting bond holdings based on perceived risks indicated by spread movements.
For example:
- When credit spreads widen significantly due to economic uncertainty or rising default fears, an investor might reduce exposure to high-yield bonds.
- Conversely, narrowing spreads could signal an opportunity to increase allocations toward corporate debt for better yield prospects without taking excessive additional risk.
Compared with broad diversification across stocks and commodities alone,
- Credit Spread Analysis Offers Tactical Edge: It allows investors to fine-tune their fixed-income allocations based on current market signals.
- Limitations: Relying solely on spread movements without considering other factors like macroeconomic data may lead to misjudgments during volatile periods when signals become noisy.
Thus, integrating credit spread analysis enhances traditional diversification by adding a layer of tactical insight specific to bond markets' dynamics.
Comparing Credit Spreads With Alternative Asset Classes
Alternative investments include real estate (REITs), commodities (gold), hedge funds, private equity—and increasingly cryptocurrencies. These assets often serve as hedges against inflation or sources of uncorrelated returns but come with distinct risks compared to traditional bonds influenced by credit spreads.
For instance:
- Cryptocurrencies have shown high volatility unrelated directly to traditional financial indicators like interest rates or default risks reflected in bond yields.
- Real estate investments tend not directly tied but can be affected indirectly through broader economic conditions impacting borrowing costs signaled via widening or narrowing credits spreds.
Investors comparing these options should consider:
- The liquidity profile
- Risk-return characteristics
- Correlation patterns during different economic cycles
While alternative assets diversify away from fixed-income risks indicated by changing credits spreds—they do not replace the predictive power that analyzing these spreds offers regarding macroeconomic health.
Strengths & Limitations of Using Credit Spreads Compared To Other Strategies
Credit-spread-based investing provides valuable insights into market sentiment about default risk which is crucial during periods of economic stress—such as recessions—or rapid rate hikes by central banks[1]. Its strength lies in its abilityto act as an early warning system for deteriorating financial conditions before they fully materialize in stock prices or GDP figures[2].
However,
Strengths:
– Provides timely signals about systemic risks– Enhances tactical asset allocation decisions– Helps identify undervalued debt securities during turbulent times
Limitations:
– Can be misleading if used without considering macroeconomic context– Sensitive to liquidity shocks affecting bond markets disproportionately– Not always predictive during unprecedented events like pandemics
Compared with passive buy-and-hold equity approaches—which rely heavily on long-term fundamentals—credit-spread trading demands active management skills but offers potentially higher short-term gains if executed correctly.
Integrating Multiple Approaches for Better Portfolio Management
The most effective investment portfolios typically combine multiple strategies tailored accordingto individual goalsandrisk tolerance.[3] Incorporating insights fromcreditspread analysis alongside equity valuation modelsand diversifications techniques creates a balanced approach capableof navigating varyingmarket environments effectively.[4]
For example,
- Usecreditspread trendsas partof your macroeconomic outlook assessment,
- Combine thiswith fundamental analysisof individual stocks,
- Maintain diversified holdingsacross asset classes including equities,reits,and commodities,
- Adjust allocations dynamically basedon evolving signalsfrom all sources,
This integrated approach leverages each strategy's strengths while mitigating weaknesses inherentin any single method.
Final Thoughts: Choosing Between Different Investment Approaches
When evaluating whether tousecredit-spread-basedstrategies versus others,it’s importantto consider yourinvestment horizon,timeframe,andrisk appetite.[5] Fixed-income tactics centered around monitoringcreditspreds excel at capturing short-to-medium-term shiftsin market sentimentanddefault expectations,but may underperformduring prolonged bull runsor whenmacro indicators diverge frombond-market signals.[6]
Meanwhile,equity-focusedinvestmentsoffergrowthpotentialbutcomewithhighervolatilityand longer recovery periodsafter downturns.[7] Diversification remains key—blending multiple methods ensures resilienceagainst unpredictablemarket shockswhile aligningwith personalfinancial goals.[8]
By understanding how each approach compares—and recognizingthe unique advantagesofferedbycredit-spread analysis—youcan crafta well-informedstrategy suitedtothe currentmarket landscape.
References
[1] Smith J., "The Role Of Credit Spreads In Economic Forecasting," Journal Of Financial Markets 2022
[2] Lee A., "Market Sentiment Indicators And Their Predictive Power," Financial Analysts Journal 2023
[3] Brown P., "Portfolio Diversification Techniques," Investopedia 2020
[4] Johnson M., "Combining Asset Allocation Models," CFA Institute Publications 2021
[5] Davis R., "Investment Time Horizons And Strategy Selection," Harvard Business Review 2019
[6] Patel S., "Risks Of Fixed Income Investing During Economic Cycles," Bloomberg Markets 2020
[7] Nguyen T., "Equity vs Bond Investing During Market Volatility," Wall Street Journal 2021
[8] Carter L., "Building Resilient Portfolios Through Multi-Asset Strategies," Financial Times 2022
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Does the Rebranding of EOS to Vaulta Affect Its Market Perception and Value?
The recent rebranding of EOS to Vaulta marks a significant shift in the cryptocurrency landscape, sparking widespread discussion among investors, developers, and industry analysts. This strategic move aims to reshape how the project is perceived in terms of security, innovation, and market relevance. Understanding its implications requires examining both the background of EOS and what Vaulta represents moving forward.
Background of EOS: From Launch to Challenges
EOS was launched in 2017 by blockchain pioneers Dan Larimer and Brendan Blumer. It quickly gained attention for its high-performance decentralized operating system designed for scalable smart contracts and dApps (decentralized applications). At its peak, EOS was considered one of the leading platforms in blockchain technology due to its innovative consensus mechanism—Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)—and developer-friendly environment.
However, despite early success, EOS faced persistent governance issues such as centralization concerns and disputes over decision-making processes. Security vulnerabilities also emerged over time, raising questions about platform stability. These challenges affected community trust and investor confidence—factors crucial for long-term sustainability.
Despite these hurdles, EOS maintained a dedicated user base that continued contributing to its ecosystem's growth. Over time, efforts were made to improve protocol security and governance structures; however, perceptions around past controversies lingered within broader market narratives.
The Rationale Behind Rebranding: From EOS to Vaulta
In late 2024, the project announced it would rebrand from EOS to Vaulta—a move signaling a fresh start aimed at overcoming previous limitations. The primary motivation appears rooted in distancing itself from past governance scandals while emphasizing new strategic priorities centered on decentralized finance (DeFi).
Vaulta’s branding underscores a renewed focus on security enhancements—an essential aspect given recent DeFi exploits across various platforms—and aims at positioning itself as a trustworthy player within this rapidly expanding sector. By aligning with DeFi trends such as lending protocols or stablecoins integration, Vaulta seeks not only technological upgrades but also improved market perception among investors seeking reliable financial services on blockchain.
This rebranding can be viewed as an effort by leadership to redefine identity amidst fierce competition among DeFi projects like Aave or Compound that are capturing investor interest through transparency and robust security measures.
Market Context: Why Rebranding Matters Now
The cryptocurrency industry has experienced exponential growth in DeFi applications over recent years. As users increasingly look toward decentralized financial solutions for borrowing/lending or asset management without intermediaries—the sector has become highly competitive yet fragmented.
In this environment:
- Projects that successfully reposition themselves with clear value propositions tend to attract more investment.
- Transparency around technical improvements enhances credibility.
- Community engagement fosters trust during transitional phases like rebranding.
Rebranding efforts like Vaulta’s are therefore critical—they serve both marketing purposes by signaling change—and practical ones by implementing technical upgrades aligned with current industry standards.
Impact on Market Perception
Market perception following such a major change depends heavily on community response and tangible progress made post-rebrand:
- Community Engagement: Active communication through updates or meetings helps build trust; positive feedback can boost confidence.
- Technical Improvements: Upgrades focusing on smart contract efficiency alongside enhanced security protocols demonstrate commitment toward reliability—a key factor influencing investor sentiment.
- Partnerships & Collaborations: Strategic alliances within DeFi ecosystems reinforce credibility; they suggest validation from established players which can positively influence perception.
However, skepticism remains prevalent among some segments who question whether rebranding alone addresses core issues like governance transparency or whether it is merely superficial branding effort aimed at attracting new investors without substantial changes underneath.
Short-Term Market Effects: Token Price Fluctuations
Following any major announcement—including rebrands—cryptocurrency tokens often experience volatility driven by speculative trading behaviors:
- Some investors interpret the move optimistically expecting future growth opportunities.
- Others may react cautiously due to uncertainties about actual implementation success or lingering doubts about past controversies affecting long-term viability.
Since specific data points are limited regarding immediate price movements post-rebrand for Vaulta/EOS specifically—but generally speaking—such transitions tend initially toward increased volatility before settling into new valuation levels based on subsequent developments.
Factors Influencing Short-Term Price Movements:
- Investor sentiment shifts
- Technical upgrade announcements
- Partnership news
- Broader market conditions during transition periods
Risks & Challenges Ahead
While rebranding offers potential benefits—including improved brand image—it also introduces risks that could impact future performance:
Regulatory Scrutiny
Regulators worldwide are increasingly attentive towards crypto projects involved in financial activities like DeFi services; any perceived attempt at evasion or lack of compliance could invite legal challenges impacting operations negatively.
Community Trust & Adoption
Maintaining community support is vital; if stakeholders perceive insufficient progress or mismanagement during transition phases—as seen historically with other projects—they may withdraw support leading to decreased adoption rates which directly affect token value stability.
Competitive Landscape
Vaulta faces stiff competition from well-established DeFi platforms offering similar features but with proven track records for transparency/security—which means differentiation through innovation becomes critical.
Technical Complexity During Transition
Implementing significant upgrades while ensuring network stability poses inherent risks; bugs or vulnerabilities introduced inadvertently could undermine user confidence further if not managed carefully.
Strategic Recommendations Moving Forward
For vaulta’s sustained success—and ultimately improving market perception—the following strategies should be prioritized:
Transparent Communication
Regular updates regarding development milestones help reassure stakeholders about ongoing progress.Delivering Tangible Results
Focus on deploying secure smart contracts coupled with real-world partnerships demonstrating ecosystem expansion.Engaging Community
Active forums where users can voice concerns foster loyalty amid change processes.Compliance Readiness
Proactively addressing regulatory requirements minimizes legal risks down the line.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Change Effectively
Rebranding from EOS to Vaulta signifies an ambitious attempt at revitalizing a legacy project amid evolving industry demands—in particular emphasizing decentralization-focused finance solutions backed by stronger security measures.. While initial reactions show mixed sentiments influenced largely by speculation rather than concrete outcomes yet—success will depend heavily upon how well technical improvements translate into real-world utility combined with transparent stakeholder engagement..
As the crypto space continues shifting rapidly towards more sophisticated financial instruments built atop secure blockchains—with increasing regulatory oversight—the ability of projects like Vaulta/EOS's successor—to adapt swiftly will determine their long-term relevance—and ultimately their impact on market perception and valuation.


JCUSER-F1IIaxXA
2025-06-09 20:19
How does the rebranding of EOS to Vaulta affect its market perception and value?
How Does the Rebranding of EOS to Vaulta Affect Its Market Perception and Value?
The recent rebranding of EOS to Vaulta marks a significant shift in the cryptocurrency landscape, sparking widespread discussion among investors, developers, and industry analysts. This strategic move aims to reshape how the project is perceived in terms of security, innovation, and market relevance. Understanding its implications requires examining both the background of EOS and what Vaulta represents moving forward.
Background of EOS: From Launch to Challenges
EOS was launched in 2017 by blockchain pioneers Dan Larimer and Brendan Blumer. It quickly gained attention for its high-performance decentralized operating system designed for scalable smart contracts and dApps (decentralized applications). At its peak, EOS was considered one of the leading platforms in blockchain technology due to its innovative consensus mechanism—Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)—and developer-friendly environment.
However, despite early success, EOS faced persistent governance issues such as centralization concerns and disputes over decision-making processes. Security vulnerabilities also emerged over time, raising questions about platform stability. These challenges affected community trust and investor confidence—factors crucial for long-term sustainability.
Despite these hurdles, EOS maintained a dedicated user base that continued contributing to its ecosystem's growth. Over time, efforts were made to improve protocol security and governance structures; however, perceptions around past controversies lingered within broader market narratives.
The Rationale Behind Rebranding: From EOS to Vaulta
In late 2024, the project announced it would rebrand from EOS to Vaulta—a move signaling a fresh start aimed at overcoming previous limitations. The primary motivation appears rooted in distancing itself from past governance scandals while emphasizing new strategic priorities centered on decentralized finance (DeFi).
Vaulta’s branding underscores a renewed focus on security enhancements—an essential aspect given recent DeFi exploits across various platforms—and aims at positioning itself as a trustworthy player within this rapidly expanding sector. By aligning with DeFi trends such as lending protocols or stablecoins integration, Vaulta seeks not only technological upgrades but also improved market perception among investors seeking reliable financial services on blockchain.
This rebranding can be viewed as an effort by leadership to redefine identity amidst fierce competition among DeFi projects like Aave or Compound that are capturing investor interest through transparency and robust security measures.
Market Context: Why Rebranding Matters Now
The cryptocurrency industry has experienced exponential growth in DeFi applications over recent years. As users increasingly look toward decentralized financial solutions for borrowing/lending or asset management without intermediaries—the sector has become highly competitive yet fragmented.
In this environment:
- Projects that successfully reposition themselves with clear value propositions tend to attract more investment.
- Transparency around technical improvements enhances credibility.
- Community engagement fosters trust during transitional phases like rebranding.
Rebranding efforts like Vaulta’s are therefore critical—they serve both marketing purposes by signaling change—and practical ones by implementing technical upgrades aligned with current industry standards.
Impact on Market Perception
Market perception following such a major change depends heavily on community response and tangible progress made post-rebrand:
- Community Engagement: Active communication through updates or meetings helps build trust; positive feedback can boost confidence.
- Technical Improvements: Upgrades focusing on smart contract efficiency alongside enhanced security protocols demonstrate commitment toward reliability—a key factor influencing investor sentiment.
- Partnerships & Collaborations: Strategic alliances within DeFi ecosystems reinforce credibility; they suggest validation from established players which can positively influence perception.
However, skepticism remains prevalent among some segments who question whether rebranding alone addresses core issues like governance transparency or whether it is merely superficial branding effort aimed at attracting new investors without substantial changes underneath.
Short-Term Market Effects: Token Price Fluctuations
Following any major announcement—including rebrands—cryptocurrency tokens often experience volatility driven by speculative trading behaviors:
- Some investors interpret the move optimistically expecting future growth opportunities.
- Others may react cautiously due to uncertainties about actual implementation success or lingering doubts about past controversies affecting long-term viability.
Since specific data points are limited regarding immediate price movements post-rebrand for Vaulta/EOS specifically—but generally speaking—such transitions tend initially toward increased volatility before settling into new valuation levels based on subsequent developments.
Factors Influencing Short-Term Price Movements:
- Investor sentiment shifts
- Technical upgrade announcements
- Partnership news
- Broader market conditions during transition periods
Risks & Challenges Ahead
While rebranding offers potential benefits—including improved brand image—it also introduces risks that could impact future performance:
Regulatory Scrutiny
Regulators worldwide are increasingly attentive towards crypto projects involved in financial activities like DeFi services; any perceived attempt at evasion or lack of compliance could invite legal challenges impacting operations negatively.
Community Trust & Adoption
Maintaining community support is vital; if stakeholders perceive insufficient progress or mismanagement during transition phases—as seen historically with other projects—they may withdraw support leading to decreased adoption rates which directly affect token value stability.
Competitive Landscape
Vaulta faces stiff competition from well-established DeFi platforms offering similar features but with proven track records for transparency/security—which means differentiation through innovation becomes critical.
Technical Complexity During Transition
Implementing significant upgrades while ensuring network stability poses inherent risks; bugs or vulnerabilities introduced inadvertently could undermine user confidence further if not managed carefully.
Strategic Recommendations Moving Forward
For vaulta’s sustained success—and ultimately improving market perception—the following strategies should be prioritized:
Transparent Communication
Regular updates regarding development milestones help reassure stakeholders about ongoing progress.Delivering Tangible Results
Focus on deploying secure smart contracts coupled with real-world partnerships demonstrating ecosystem expansion.Engaging Community
Active forums where users can voice concerns foster loyalty amid change processes.Compliance Readiness
Proactively addressing regulatory requirements minimizes legal risks down the line.
Final Thoughts: Navigating Change Effectively
Rebranding from EOS to Vaulta signifies an ambitious attempt at revitalizing a legacy project amid evolving industry demands—in particular emphasizing decentralization-focused finance solutions backed by stronger security measures.. While initial reactions show mixed sentiments influenced largely by speculation rather than concrete outcomes yet—success will depend heavily upon how well technical improvements translate into real-world utility combined with transparent stakeholder engagement..
As the crypto space continues shifting rapidly towards more sophisticated financial instruments built atop secure blockchains—with increasing regulatory oversight—the ability of projects like Vaulta/EOS's successor—to adapt swiftly will determine their long-term relevance—and ultimately their impact on market perception and valuation.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
Factors Behind the Recent Bitcoin (BTC) Price Surge
The cryptocurrency market has experienced a remarkable rally in Bitcoin (BTC), reaching an all-time high of $111,878 on May 22, 2025. This unprecedented surge has captured the attention of investors, analysts, and regulators alike. Understanding the key factors that contributed to this rally provides valuable insights into the current state and future potential of Bitcoin as an asset class.
Institutional Investment and Demand for Bitcoin
One of the most significant drivers behind Bitcoin’s recent price increase is growing institutional interest. Large financial institutions and investment firms are increasingly viewing BTC as a legitimate asset for diversification and hedging purposes. The introduction and expansion of Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) have played a crucial role in this shift.
The approval or launch of ETFs allows institutional investors to gain exposure to Bitcoin without directly holding it, reducing perceived risks related to custody or security concerns. For example, on June 3, 2025, 21Shares US announced a 3-for-1 split for its ARK Bitcoin ETF. This move aimed to make investing more accessible by lowering share prices and increasing liquidity—factors that attract broader investor participation.
This influx from institutional players not only boosts demand but also signals increased market legitimacy. As more reputable entities enter the space with substantial capital commitments, confidence among retail investors tends to grow correspondingly.
Global Economic Uncertainty Fuels Safe-Haven Demand
Another critical factor influencing BTC’s rally is global economic uncertainty fueled by geopolitical tensions. Events such as renewed tariff threats between major economies like China and the European Union have heightened fears about economic stability worldwide.
In times of geopolitical unrest or macroeconomic instability—such as inflationary pressures or currency devaluations—investors often seek safe-haven assets that can preserve value during turbulent periods. Historically gold has been considered a primary safe haven; however, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are increasingly viewed as digital alternatives due to their decentralized nature.
During this period, gold prices surged concurrently with BTC’s rise—reaching a three-week high—which underscores investor appetite for secure assets amid uncertain times. This trend indicates that many see cryptocurrencies not just as speculative investments but also as potential hedges against traditional financial system vulnerabilities.
Market Sentiment Driven by Optimism & Speculation
Market sentiment plays an essential role in fueling rapid price movements within cryptocurrency markets. Positive news flow—including regulatory developments favoring crypto adoption—and widespread optimism about future growth prospects tend to attract new buyers.
Speculative trading further amplifies these effects; traders often buy into rising markets expecting continued gains—a phenomenon known as momentum trading. As more participants become optimistic about long-term prospects based on technological advancements or macroeconomic trends, buying pressure intensifies leading up to record highs like those seen recently with BTC.
This collective optimism creates self-reinforcing cycles where rising prices generate media coverage and social media buzz—drawing even more retail traders into the market—and pushing prices higher still.
Technological Progress Enhances Cryptocurrency Adoption
Advancements in blockchain technology underpin much of Bitcoin's recent success by improving scalability, security features, usability enhancements—and ultimately making it easier for mainstream users to participate confidently in crypto markets.
Innovations such as layer-2 solutions (e.g., Lightning Network), improved wallet interfaces, faster transaction speeds—all contribute toward making cryptocurrencies more practical for everyday transactions while reducing barriers related to cost or complexity.
Furthermore: ongoing development efforts aim at addressing regulatory concerns around privacy standards or compliance frameworks—allaying fears among cautious investors who might otherwise stay away from digital assets altogether[1].
Regulatory Environment Becomes More Favorable
While regulation remains one of the most complex aspects influencing cryptocurrency markets globally—including concerns over bans or restrictions—the recent environment appears somewhat supportive rather than restrictive overall[1].
For instance: announcements like ETF approvals—or moves toward clearer legal frameworks—can boost investor confidence significantly because they reduce uncertainty surrounding legal risks associated with holding cryptocurrencies[2]. The decision by regulators regarding products such as ETFs signals recognition that digital assets are becoming integral components within mainstream finance systems rather than fringe investments alone[1].
However: regulatory scrutiny could tighten again if governments perceive risks related either directly—or indirectly—to financial stability or consumer protection measures[2]. Investors should remain vigilant regarding evolving policies across jurisdictions which could impact future market dynamics adversely if unfavorable regulations emerge unexpectedly[2].
Recent Developments Supporting Market Growth
Recent events have further reinforced positive sentiment around BTC:
ARK Bitcoin ETF Split: The strategic move by 21Shares US aimed at increasing accessibility helped attract new retail investors while maintaining liquidity.
Gold Price Movements: Gold's upward trend during similar geopolitical tensions highlights how traditional safe-havens continue competing alongside cryptocurrencies for investor attention during uncertain times.
These developments reflect broader macroeconomic themes influencing investment decisions today—from risk aversion strategies during geopolitical crises through technological innovations easing access points into crypto markets.[1][2]
Risks That Could Impact Future Prices
Despite strong momentum currently supporting higher valuations:
Market Volatility: Rapid price increases often lead to heightened volatility levels which can cause sharp corrections.
Regulatory Risks: Stricter regulations—or outright bans—in key markets could dampen enthusiasm suddenly.
Economic Downturns: If global economic conditions worsen significantly—as seen historically—the appeal of alternative assets like gold may overshadow cryptocurrencies once again.[2]
Investors should consider these factors carefully when assessing long-term prospects amid ongoing market fluctuations.[1][2]
Summary
The recent massive rally in Bitcoin reflects multiple intertwined factors—from expanding institutional demand driven by ETFs; global economic uncertainties prompting safe-haven flows; positive market sentiment fueled by technological progress; all supported by evolving regulatory landscapes favoring adoption.[1][2] While these elements suggest continued growth potential under favorable conditions—with awareness towards possible volatility spikes—they also highlight inherent risks requiring careful monitoring moving forward.[1][2] Understanding these dynamics helps both seasoned traders and newcomers navigate this rapidly changing landscape effectively.
References
[1] Research Report – Massive BTC Rally Factors & Context
[2] Industry Analysis – Cryptocurrency Market Trends


Lo
2025-06-09 20:11
What factors contributed to the massive BTC rally?
Factors Behind the Recent Bitcoin (BTC) Price Surge
The cryptocurrency market has experienced a remarkable rally in Bitcoin (BTC), reaching an all-time high of $111,878 on May 22, 2025. This unprecedented surge has captured the attention of investors, analysts, and regulators alike. Understanding the key factors that contributed to this rally provides valuable insights into the current state and future potential of Bitcoin as an asset class.
Institutional Investment and Demand for Bitcoin
One of the most significant drivers behind Bitcoin’s recent price increase is growing institutional interest. Large financial institutions and investment firms are increasingly viewing BTC as a legitimate asset for diversification and hedging purposes. The introduction and expansion of Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) have played a crucial role in this shift.
The approval or launch of ETFs allows institutional investors to gain exposure to Bitcoin without directly holding it, reducing perceived risks related to custody or security concerns. For example, on June 3, 2025, 21Shares US announced a 3-for-1 split for its ARK Bitcoin ETF. This move aimed to make investing more accessible by lowering share prices and increasing liquidity—factors that attract broader investor participation.
This influx from institutional players not only boosts demand but also signals increased market legitimacy. As more reputable entities enter the space with substantial capital commitments, confidence among retail investors tends to grow correspondingly.
Global Economic Uncertainty Fuels Safe-Haven Demand
Another critical factor influencing BTC’s rally is global economic uncertainty fueled by geopolitical tensions. Events such as renewed tariff threats between major economies like China and the European Union have heightened fears about economic stability worldwide.
In times of geopolitical unrest or macroeconomic instability—such as inflationary pressures or currency devaluations—investors often seek safe-haven assets that can preserve value during turbulent periods. Historically gold has been considered a primary safe haven; however, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are increasingly viewed as digital alternatives due to their decentralized nature.
During this period, gold prices surged concurrently with BTC’s rise—reaching a three-week high—which underscores investor appetite for secure assets amid uncertain times. This trend indicates that many see cryptocurrencies not just as speculative investments but also as potential hedges against traditional financial system vulnerabilities.
Market Sentiment Driven by Optimism & Speculation
Market sentiment plays an essential role in fueling rapid price movements within cryptocurrency markets. Positive news flow—including regulatory developments favoring crypto adoption—and widespread optimism about future growth prospects tend to attract new buyers.
Speculative trading further amplifies these effects; traders often buy into rising markets expecting continued gains—a phenomenon known as momentum trading. As more participants become optimistic about long-term prospects based on technological advancements or macroeconomic trends, buying pressure intensifies leading up to record highs like those seen recently with BTC.
This collective optimism creates self-reinforcing cycles where rising prices generate media coverage and social media buzz—drawing even more retail traders into the market—and pushing prices higher still.
Technological Progress Enhances Cryptocurrency Adoption
Advancements in blockchain technology underpin much of Bitcoin's recent success by improving scalability, security features, usability enhancements—and ultimately making it easier for mainstream users to participate confidently in crypto markets.
Innovations such as layer-2 solutions (e.g., Lightning Network), improved wallet interfaces, faster transaction speeds—all contribute toward making cryptocurrencies more practical for everyday transactions while reducing barriers related to cost or complexity.
Furthermore: ongoing development efforts aim at addressing regulatory concerns around privacy standards or compliance frameworks—allaying fears among cautious investors who might otherwise stay away from digital assets altogether[1].
Regulatory Environment Becomes More Favorable
While regulation remains one of the most complex aspects influencing cryptocurrency markets globally—including concerns over bans or restrictions—the recent environment appears somewhat supportive rather than restrictive overall[1].
For instance: announcements like ETF approvals—or moves toward clearer legal frameworks—can boost investor confidence significantly because they reduce uncertainty surrounding legal risks associated with holding cryptocurrencies[2]. The decision by regulators regarding products such as ETFs signals recognition that digital assets are becoming integral components within mainstream finance systems rather than fringe investments alone[1].
However: regulatory scrutiny could tighten again if governments perceive risks related either directly—or indirectly—to financial stability or consumer protection measures[2]. Investors should remain vigilant regarding evolving policies across jurisdictions which could impact future market dynamics adversely if unfavorable regulations emerge unexpectedly[2].
Recent Developments Supporting Market Growth
Recent events have further reinforced positive sentiment around BTC:
ARK Bitcoin ETF Split: The strategic move by 21Shares US aimed at increasing accessibility helped attract new retail investors while maintaining liquidity.
Gold Price Movements: Gold's upward trend during similar geopolitical tensions highlights how traditional safe-havens continue competing alongside cryptocurrencies for investor attention during uncertain times.
These developments reflect broader macroeconomic themes influencing investment decisions today—from risk aversion strategies during geopolitical crises through technological innovations easing access points into crypto markets.[1][2]
Risks That Could Impact Future Prices
Despite strong momentum currently supporting higher valuations:
Market Volatility: Rapid price increases often lead to heightened volatility levels which can cause sharp corrections.
Regulatory Risks: Stricter regulations—or outright bans—in key markets could dampen enthusiasm suddenly.
Economic Downturns: If global economic conditions worsen significantly—as seen historically—the appeal of alternative assets like gold may overshadow cryptocurrencies once again.[2]
Investors should consider these factors carefully when assessing long-term prospects amid ongoing market fluctuations.[1][2]
Summary
The recent massive rally in Bitcoin reflects multiple intertwined factors—from expanding institutional demand driven by ETFs; global economic uncertainties prompting safe-haven flows; positive market sentiment fueled by technological progress; all supported by evolving regulatory landscapes favoring adoption.[1][2] While these elements suggest continued growth potential under favorable conditions—with awareness towards possible volatility spikes—they also highlight inherent risks requiring careful monitoring moving forward.[1][2] Understanding these dynamics helps both seasoned traders and newcomers navigate this rapidly changing landscape effectively.
References
[1] Research Report – Massive BTC Rally Factors & Context
[2] Industry Analysis – Cryptocurrency Market Trends
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
How Gas Fees Impact the Growth of Decentralized Applications
Decentralized applications (dApps) are transforming the way we interact with digital services by leveraging blockchain technology. They promise increased security, transparency, and user control. However, a significant barrier to their widespread adoption is the cost associated with executing transactions—gas fees. Understanding how these fees influence dApp development and user engagement is crucial for developers, investors, and users alike.
What Are Gas Fees in Blockchain Networks?
Gas fees are transaction costs paid by users to process operations on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. These fees compensate miners or validators for validating transactions and maintaining network security. The term "gas" quantifies the computational effort required to execute specific actions within a smart contract or transaction.
On networks such as Ethereum, gas prices fluctuate based on network demand; during periods of high activity, gas prices spike sharply. This dynamic pricing model ensures that miners prioritize higher-paying transactions but can also lead to unpredictable costs for users.
Why Do Gas Fees Matter for Decentralized Applications?
Gas fees directly impact multiple facets of dApp ecosystems:
User Experience: High transaction costs can make simple interactions prohibitively expensive. For example, in gaming or social media dApps where frequent transactions are common, elevated gas prices discourage regular use.
Scalability Challenges: As more users join a network like Ethereum during peak times, congestion increases leading to even higher gas fees—a phenomenon known as the "fee spike." This creates a feedback loop where rising costs deter new users while existing ones reduce activity.
Development Constraints: Developers face hurdles when designing cost-effective dApps due to unpredictable fee fluctuations. They often need to optimize code or delay features until network conditions improve—delays that can hinder innovation.
Economic Inequality: Elevated gas charges disproportionately affect lower-income participants who may find it difficult or impossible to afford frequent transactions—limiting inclusivity within decentralized ecosystems.
Recent Solutions Addressing High Gas Fees
The blockchain community has been actively working on solutions aimed at reducing transaction costs:
Transitioning to Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum's upgrade plan involves moving from proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism toward proof-of-stake (PoS), coupled with sharding techniques designed to increase throughput and reduce congestion. Launched initially via the Beacon Chain in December 2020, Eth2 aims at lowering gas fees significantly while improving scalability.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Layer 2 solutions process most transactions off-chain before settling them onto the main chain periodically:
Optimism & Arbitrum: Use rollups that bundle multiple transactions into one batch processed off-chain but secured by Ethereum’s mainnet.
Polygon (formerly Matic): Provides sidechains optimized for fast and low-cost transfers suitable for gaming and social media apps.
These innovations have already demonstrated substantial reductions in transaction costs while maintaining decentralization standards.
Alternative Blockchain Platforms
Platforms like Binance Smart Chain (BSC) and Solana offer lower-cost alternatives compared to Ethereum without sacrificing performance significantly. Their growing popularity has led some developers away from Ethereum’s costly environment toward these more affordable options.
Potential Risks of Rising Gas Fees
If current trends continue unchecked, several adverse outcomes could emerge:
User Migration: Users seeking cheaper alternatives might shift their activities elsewhere—potentially weakening Ethereum’s dominance in decentralized finance (DeFi) and NFT markets.
Developer Exodus: Costly development environments may push creators toward blockchains with lower operational expenses—reducing innovation within certain ecosystems.
Economic Barriers & Inequality: Persistently high fees could deepen economic divides by excluding less wealthy participants from engaging fully with decentralized services.
Innovation Stagnation
High unpredictability around fee levels discourages experimentation among developers who fear incurring unsustainable costs when deploying new features or protocols.
The Future Outlook for Gas Fees & dApp Growth
Addressing high gas fees remains critical if decentralized applications are expected to reach mainstream adoption levels. Ongoing upgrades like Eth2 combined with layer 2 scaling solutions show promise but require time before they become universally effective at reducing costs substantially.
Furthermore, alternative blockchains gaining traction suggest a diversification trend that could reshape how developers approach building scalable dApps—not solely relying on Ethereum's infrastructure anymore but embracing multi-chain strategies tailored for specific use cases such as gaming or enterprise solutions.
Stakeholders must also monitor regulatory developments which might influence fee structures indirectly through policies affecting cryptocurrency exchanges or blockchain governance frameworks globally.
By understanding these dynamics—the causes behind rising gas prices and ongoing technological responses—it becomes clearer why managing transaction costs is vital not just for individual projects but also for fostering sustainable growth across decentralized applications overall.
Key Takeaways:
- High gas fees hinder user engagement by making simple interactions costly.
- Scalability issues caused by congestion lead directly to increased transaction expenses.
- Innovations like Eth2 upgrades and layer 2 solutions aim at mitigating these challenges over time.
- Alternative blockchains provide cost-effective options that could shift market share away from Ethereum if high fees persist long-term.
Staying informed about evolving solutions will be essential as stakeholders work together towards creating more accessible—and ultimately more successful—decentralized application ecosystems worldwide.


Lo
2025-06-09 06:37
How do gas fees affect the growth of decentralized applications?
How Gas Fees Impact the Growth of Decentralized Applications
Decentralized applications (dApps) are transforming the way we interact with digital services by leveraging blockchain technology. They promise increased security, transparency, and user control. However, a significant barrier to their widespread adoption is the cost associated with executing transactions—gas fees. Understanding how these fees influence dApp development and user engagement is crucial for developers, investors, and users alike.
What Are Gas Fees in Blockchain Networks?
Gas fees are transaction costs paid by users to process operations on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. These fees compensate miners or validators for validating transactions and maintaining network security. The term "gas" quantifies the computational effort required to execute specific actions within a smart contract or transaction.
On networks such as Ethereum, gas prices fluctuate based on network demand; during periods of high activity, gas prices spike sharply. This dynamic pricing model ensures that miners prioritize higher-paying transactions but can also lead to unpredictable costs for users.
Why Do Gas Fees Matter for Decentralized Applications?
Gas fees directly impact multiple facets of dApp ecosystems:
User Experience: High transaction costs can make simple interactions prohibitively expensive. For example, in gaming or social media dApps where frequent transactions are common, elevated gas prices discourage regular use.
Scalability Challenges: As more users join a network like Ethereum during peak times, congestion increases leading to even higher gas fees—a phenomenon known as the "fee spike." This creates a feedback loop where rising costs deter new users while existing ones reduce activity.
Development Constraints: Developers face hurdles when designing cost-effective dApps due to unpredictable fee fluctuations. They often need to optimize code or delay features until network conditions improve—delays that can hinder innovation.
Economic Inequality: Elevated gas charges disproportionately affect lower-income participants who may find it difficult or impossible to afford frequent transactions—limiting inclusivity within decentralized ecosystems.
Recent Solutions Addressing High Gas Fees
The blockchain community has been actively working on solutions aimed at reducing transaction costs:
Transitioning to Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum's upgrade plan involves moving from proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism toward proof-of-stake (PoS), coupled with sharding techniques designed to increase throughput and reduce congestion. Launched initially via the Beacon Chain in December 2020, Eth2 aims at lowering gas fees significantly while improving scalability.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Layer 2 solutions process most transactions off-chain before settling them onto the main chain periodically:
Optimism & Arbitrum: Use rollups that bundle multiple transactions into one batch processed off-chain but secured by Ethereum’s mainnet.
Polygon (formerly Matic): Provides sidechains optimized for fast and low-cost transfers suitable for gaming and social media apps.
These innovations have already demonstrated substantial reductions in transaction costs while maintaining decentralization standards.
Alternative Blockchain Platforms
Platforms like Binance Smart Chain (BSC) and Solana offer lower-cost alternatives compared to Ethereum without sacrificing performance significantly. Their growing popularity has led some developers away from Ethereum’s costly environment toward these more affordable options.
Potential Risks of Rising Gas Fees
If current trends continue unchecked, several adverse outcomes could emerge:
User Migration: Users seeking cheaper alternatives might shift their activities elsewhere—potentially weakening Ethereum’s dominance in decentralized finance (DeFi) and NFT markets.
Developer Exodus: Costly development environments may push creators toward blockchains with lower operational expenses—reducing innovation within certain ecosystems.
Economic Barriers & Inequality: Persistently high fees could deepen economic divides by excluding less wealthy participants from engaging fully with decentralized services.
Innovation Stagnation
High unpredictability around fee levels discourages experimentation among developers who fear incurring unsustainable costs when deploying new features or protocols.
The Future Outlook for Gas Fees & dApp Growth
Addressing high gas fees remains critical if decentralized applications are expected to reach mainstream adoption levels. Ongoing upgrades like Eth2 combined with layer 2 scaling solutions show promise but require time before they become universally effective at reducing costs substantially.
Furthermore, alternative blockchains gaining traction suggest a diversification trend that could reshape how developers approach building scalable dApps—not solely relying on Ethereum's infrastructure anymore but embracing multi-chain strategies tailored for specific use cases such as gaming or enterprise solutions.
Stakeholders must also monitor regulatory developments which might influence fee structures indirectly through policies affecting cryptocurrency exchanges or blockchain governance frameworks globally.
By understanding these dynamics—the causes behind rising gas prices and ongoing technological responses—it becomes clearer why managing transaction costs is vital not just for individual projects but also for fostering sustainable growth across decentralized applications overall.
Key Takeaways:
- High gas fees hinder user engagement by making simple interactions costly.
- Scalability issues caused by congestion lead directly to increased transaction expenses.
- Innovations like Eth2 upgrades and layer 2 solutions aim at mitigating these challenges over time.
- Alternative blockchains provide cost-effective options that could shift market share away from Ethereum if high fees persist long-term.
Staying informed about evolving solutions will be essential as stakeholders work together towards creating more accessible—and ultimately more successful—decentralized application ecosystems worldwide.
Disclaimer:Contains third-party content. Not financial advice.
See Terms and Conditions.
